Business
Digital banking holds the key to financial inclusion in Nigeria – GTBank CEO, Segun Agbaje

Nigeria’s economy may be in a difficult period, but with digitalisation at the core of the national banking strategy, financial inclusion has been given room to grow
Nigeria is becoming increasingly connected thanks to digital banking
Author: SegunAgbaje, Managing Director and CEO of Guaranty Trust Bank
“There are so many people in Africa that are outside the banking system”, said SegunAgbaje, Managing Director and CEO of Guaranty Trust Bank (GTBank), one of the continent’s leading financial institutions. “For you to be part of organised society, financial inclusion is a must.”
Slowly but surely, financial inclusion in Africa is improving. In fact, the Central Bank of Nigeria predicts that, by 2020, the number of adult Nigerians with access to payment services will increase to around 70 percent (see Fig 1). “It’s not as superfast as we would like it to be, but there are marked improvements, and this is steadily increasing”, said Agbaje, speaking to World Finance. “Just 10 years ago, data on financial inclusion was hard to come by. Now we know just how much better we must do in order to expand access to financial services.”
Access to savings, credit, insurance and pensions is also growing rapidly. “Encouraging as these projections are, we know that there’s a lot more to be done. This is why, at GTBank, we are keen to leverage digital technology to expand the reach of our products and services. Mobile has become very, very big and we have begun to see people doing a lot using their mobile phones.”
Agbaje points to the example of Kenya’s M-Pesa, a mobile-based money transfer and finance platform that is now used by more than two thirds of the country’s adult population. The mobile app serves as a channel for approximately 25 percent of Kenya’s GNP. “When I look at our mobile technology compared to a lot of developed economies, I think we’re a lot further ahead. You know, I actually think that the African banking sector is very much ahead in terms of mobile banking. And I think African banks are probably embracing disruptive technologies a lot quicker, because we don’t have as many legacies.”
Making banking more mobile
This readiness to embrace new technologies has helped a large proportion of the African population skip whole stages of traditional digital development altogether. Indeed, for many, a smartphone is their first computer. Agbaje said: “From experience, we know that the major reasons for financial exclusion include the lack of physical access to financial institutions, inadequate understanding of financial institutions and their products, general distrust in the system, and the affordability of products as a result of minimum opening balance requirements.”
Despite these hurdles, technology is helping forward-thinking institutions tackle such challenges head on, prompting financial inclusion to leap forward on the African continent. Agbajeexplained: “The world is changing around us and the future of banking is digital. To protect our traditional business and maintain our social relevance, we are incorporating another model, which involves mobile phones, use of data, partnerships and collaborations. Simply put, we are creating a platform to support our traditional business model by leveraging digital solutions.”
GTBank’s Bank 737 provides banking services to millions of Nigerian mobile phone owners, and does not require internet access to perform basic banking services. Anyone with a phone registered in Nigeria can open an account, transfer money, buy airtime or check their balance by dialling *737#. The convenience of Bank 737 lies in the fact that all of its services can be accessed through a customer’s mobile phone, at the dial of *737#. And because stable internet access is still not ubiquitous in Africa, Bank 737, being USSD-powered, side steps the need for an internet connection.
“Through this service, which makes banking simpler, cheaper and faster, we continue to pull into the banking stream many of those who have long been excluded from the country’s financial framework”, said Agbaje. “Since its introduction, we have recorded an uptake of over three million customers and over NGN 1trn [$3.1bn] in transactions via the platform.
The reception of Bank 737 has been phenomenal, with it gaining recognition as Product of the Year in Africa from The Asian Banker and Best Digital Bank in Africa from Euromoney. The bank was also the recipient of six awards at the 2017 Electronic Payment Incentive Scheme Awards, which was organised by the Central Bank of Nigeria in conjunction with the Nigeria Interbank Settlement System to recognise financial institutions, merchants and other stakeholders at the forefront of driving electronic payments in Nigeria.”
Digitally minded
“Core to our digital strategy is both our understanding that the future of banking is digital, and our determination to lead that future”, Agbaje said. “We know, because digital technologies have dissolved the boundaries between industry sectors, that our competition is no longer just banks. It now includes fintechs, telcos and tech companies that can provide speed and flexibility to customers as we can. This creates tough challenges for the banking sector, but it also creates ample opportunities to extend our footprint.”
A readiness to embrace new technologies has helped large portions of the African population skip whole stages of traditional digital development altogether
For example, the bank’s SME MarketHub is an e-commerce platform that allows business owners to create online stores. Agbaje told World Finance: “Our strategy is to take advantage of the new opportunities born from the digital revolution by moving beyond our traditional role as enablers of financial transactions and providers of financial products, to playing a deeper role in the digital and commercial lives of our customers. In pursuit of this strategy we have created our own in-house fintech division, while also actively seeking partnerships and collaborations with other fintechs.
“Our immediate focus is three-pronged; to digitalise our key processes, build a robust data-gathering infrastructure, and create a well designed, segmented and integrated customerexperience, rather than a one-size-fits-all distribution. In the long run, our goal is to build a digital bank that consistently delivers faster, cheaper and better solutions for the constantly evolving needs of our customers.”
The lack of digital and electrical infrastructure, as well as lower levels of wealth than those found in more developed markets, means that there are some barriers to the full adoption of digital banking that are particular to Africa. “Another obvious challenge is the little focus given to innovation in the banking industry.
African banks, like most banks across the world, tend to innovate in bite sizes, and generally around products, rather than service delivery. It was almost as though banks believed that ownership of the customer was their right, as long as they had the branch network to support customer footfall. Now, facing the real threat of losing relevance, banks are waking up to this need to innovate – not just out of dire necessity, but as a strategic objective.”
Agbaje also pointed out that, while GTBank has made significant gains in getting customers to accept digital banking as a viable alternative to traditional forms, there is still more to be done. That said, he is hopeful that the Central Bank of Nigeria’s ‘Cash-less Nigeria’ policy, which discourages the use of cash, will drive greater migration to e-banking platforms.
“We are also tackling the innovation challenge. We now operate an open innovation policy, through which we invest significantly in building our in-house digital capabilities. At the same time, we are seeking effective partnerships and alliances to drive operational efficiency and boost our competitive advantage.
“We want to become a fully digital bank that offers everyday banking services outside of traditional bank walls, but more than that, we want to create digital touch points that ensure we are constantly interacting and playing a deep role in the lives our customers. This of course requires a sustained commitment, and we have repositioned our business structures in such a way that makes us very confident in our continued leadership of Africa’s digital frontier.”
Gaining interest
Despite the difficult business environment in 2016, GTBank enjoyed “a fairly decent year”, according to Agbaje. The bank overcame these challenges by growing its retail business and leveraging technology to deliver superior payment solutions to make banking simpler, faster and better. Gross earnings for the period grew by 37 percent to NGN 414.62bn ($1.3bn), from NGN 301.85bn ($959m) in December 2015 (see Fig 2).
This was driven primarily by growth in interest income, as well as foreign exchange income. Profit before tax stood at NGN 165.14bn ($524.7m), representing a growth of 37 percent since December 2015. The bank’s loan book also grew 16 percent, from the NGN 1.37trn ($4.4bn) recorded in December 2015 to NGN 1.59trn ($5.1bn) in December 2016, with corresponding growth in total deposits increasing 29 percent, to NGN 2.11trn ($6.7bn).
Likewise, the bank’s balance sheet remained strong with a 19.7 percent growth in total assets and contingents, reaching NGN 3.70trn ($11.8bn) at the end of December 2016, while shareholders’ funds reached NGN 504.9bn ($1.6bn). The bank’s non-performing loans remained low at 3.29 percent – below the regulatory threshold of 3.66 percent, with adequate coverage of 131.79 percent. Against the backdrop of this result, return on equity (ROE) and return on assets closed at 35.96 percent and 5.85 percent respectively.
According to Agbaje: “The vision of the bank is to build an oasis in a country that was not necessarily known for doing things properly, so we focused on ethics and integrity. And once you build anything on that type of foundation – because even though things change, values never change – and bring in very young people who imbibe this culture along with a healthy attitude towards work, you have a workforce that’s very young and dynamic, possessing all the right values to enable you to build a successful organisation.”
Pan-African
GTBank is building on its successes both at home and abroad through its ‘Pan-African’ growth strategy. Apart from its home market in Nigeria, the bank enjoys a presence in three countries in east Africa (Kenya, Rwanda and Uganda), five in the west (Ivory Coast, Gambia, Ghana, Liberia and Sierra Leone) and has plans to have another in Tanzania by the end of the year.“Our strategy has always been to go into a country and take the high end of the middle market, and then as we grow, enter into the corporate markets.
“We are building a high-end type retail business because the middle class is emerging in most countries in Africa, and where you have an emerging middle class, you have a lot of banking opportunities. So far, we have been fairly successful, delivering an ROE after tax of over 25 percent.”
The bank’s expansion strategy has enjoyed remarkable success, with businesses outside Nigeria now accounting for 15 percent of total deposits, 11 percent of its loans and around 8.2 percent of its profit. Over the next three years, Agbaje expects subsidiary contribution to grow further, to approximately 20 percent.
He told World Finance: “I’m pretty excited about the fact that the profit of the bank has grown by over 300 percent in the last five years. Our customer base has grown from around two million to over 10 million, and we have built a very strong e-business as well.
“We are driven by a vision to create a great African institution; an institution that can compete anywhere in the world in terms of good corporate governance culture and performance. We are driven by the desire to be, in terms of best practices, as good as any institution in the world. As a bank, we always want to do better than 25 percent ROE, and if we have the corporate governance that you’d find anywhere else in the world, then we’ll always be an attractive destination for discerning international investors.”
Growing the SME sector
According to Agbaje: “At GTBank, we have been enriching lives since 1990. We do this by giving people a source of livelihood, growing businesses and offering them scale and infrastructure that might not have been available to them otherwise. We are doing things that people never thought possible, and doing most of it for free. Our aim is to continuously transform our organisation into a business enterprise that is all about creating value for our customers, shareholders and the communities in which we operate.”
A key area of focus for GTBank has been widening financial access and building capacity for SMEs. “What we have found with a lot of SMEs is that the financial capacity to borrow isn’t there yet”, said Agbaje. “This is why we created the MarketHub, so that our customers can have an e-commerce platform in addition to their traditional market places so they can grow their revenues.”
Building this online economy is important for both customers and the host economy as a whole, as well as for GTBank. “If we can help increase your sales, then we increase your cash flow andwe increase your ability to repay loans. We give loans, but what people must remember is that we have no money of our own, so whatever loans we give must come back.”
As part of the bank’s long-term growth strategy, it has developed a rapidly growing SME franchise that is radically positioning the bank as the apt financial institution for small and medium-size enterprises. This is built on the bank’s understanding of the crucial role of small businesses when it comes to the sustenance of economic growth and development.
Facing the real threat of losing relevance, banks are waking up to the need to innovate – not just out of dire necessity, but as a strategic objective
“As a foremost financial institution, we have a huge obligation to our host communities: not only must we never fail, we have to remain consistent in delivering superior performance and creating value for our stakeholders. We are constantly innovating how we give back to our host communities by going beyond traditional corporate philanthropies. We intervene in key economic sectors to strengthen small businesses through non-profit, consumer-focused fairs and capacity building initiatives that serve to boost their expertise, exposure and business growth.”
In May 2016, the bank held the first of its consumer-focused initiatives: the GTBank Food and Drink Fair. The aim was to promote enterprise within the Nigerian food industry by connecting small businesses involved in the production and sale of food and food-related items to a large audience of consumers and food enthusiasts. The event hosted more than 90 exhibitors from the food sector and attracted around 25,000 guests over its two-day period.
This event was shortly followed by the GTBank Fashion Weekend in November 2016, which targeted the country’s fast-growing fashion industry. The event was a huge success, becoming a meeting point for all stakeholders in the industry and providing a space for retail exhibitions, masterclasses and runway shows.
“We plan to continue such initiatives across viable sectors where we can help small businesses boost their growth potential and productivity. These initiatives are driven by our ambition to play a deeper role in people’s social and commercial lives, thus positioning ourselves at the centre of an extended ecosystem that serves both their banking and non-banking needs, while allowing for frequent interaction between them and our organisation.”
Business
Deadline of Compliance: Nigeria’s Urgent Call for Tax Return Filing

Deadline of Compliance: Nigeria’s Urgent Call for Tax Return Filing
By George Omagbemi Sylvester | Published by SaharaWeeklyNG.com
“Shift or Structural Demand? A Declaration of Civic Duty in a Nation at a Fiscal Crossroads.”
In the unfolding narrative of national development and economic reform, few instruments are as defining as tax compliance. For Nigeria, a nation perpetually grappling with revenue shortfalls, structural dependency on a single export commodity, and entrenched informal economic behaviour, the Federal Government’s recent clarification on tax return deadlines is not mere bureaucratic noise. It is a deliberate and inescapable declaration: the social contract between citizen and state must be honoured through transparent, lawful and timely tax reporting.
At its core, the government’s pronouncement is stark in its simplicity and radical in its implications. Federal authorities, speaking through the Chairman of the Presidential Committee on Fiscal Policy and Tax Reforms, Taiwo Oyedele, have made it unequivocally clear that every Nigerian, whether employer or individual taxpayer, must file annual tax returns under the law. This encompasses self-assessment filings by individuals that too many assumed ended once employers deducted pay-as-you-earn taxes from their salaries.
This is not an optional civic suggestion, it is mandatory, backed by statute, and tied to a broader vision of national fiscal responsibility. Citizens can no longer hide behind ignorance, apathy, or false assumptions. “Many people assume that if their employer deducts tax from their salaries, their obligations end there. That is wrong,” Oyedele warned, emphasizing that the obligation to file remains with the individual under both existing and newly reformed tax laws.
The Deadlines and the Reality They Reveal.
Across the federation, state and federal revenue authorities have reaffirmed statutory deadlines in pursuit of compliance. The Lagos State Internal Revenue Service, for instance, moved to extend its filing date for employer returns by a narrow window, reflecting the reality that compliance often lags behind legal timelines. The extension was intended not as leniency, but as a pragmatic effort to allow accurate and complete submissions, underscoring that true compliance rises above mere mechanical ticking of a box.
At the federal level, Oyedele’s intervention was even more fundamental. He reminded Nigerians that annual tax returns for the preceding year must be filed in good faith, with integrity and in respect of the law. This applies regardless of income level including low-income earners who have historically believed that they are outside the tax net. “All of us must file our returns, including those earning low income,” he stated.
Herein lies one of the most challenging truths of contemporary Nigerian governance: widespread tax non-compliance is not just a technical breach of law, it is a deep cultural and structural issue that reflects decades of mistrust between citizens and the state.
The Root of the Problem: Non-Compliance as a Symptom.
Nigeria’s tax culture has long been under scrutiny. Public discourse and economic analysis consistently show that a significant majority of eligible taxpayers do not file annual returns. Oyedele highlighted that even in states widely regarded as tax administration leaders, compliance remains strikingly low, often below five percent.
This widespread non-compliance stems from multiple sources:
A long history of weak tax administration systems, where enforcement was inconsistent and penalties were rarely applied.
A perception that public services do not reflect the taxes collected, eroding the citizenry’s belief in reciprocity.
An informal economy where income often goes unrecorded, making filing seem irrelevant or impossible to many.
Lack of awareness, with many Nigerians genuinely believing that tax liability ends with employer deductions.
The government’s renewed push for compliance directly challenges these perceptions. It signals a shift from voluntary or lax compliance to structured accountability, a stance that aligns with best practices in modern public finance.
Why This Matters: Beyond Deadlines.
At its most profound level, the insistence on tax return filings is about nation-building and shared responsibility.
Scholars of public finance universally agree that a robust tax system is the backbone of sustainable development. As the eminent economist Dr. Joseph E. Stiglitz has observed, “A society that cannot mobilize its own resources through fair taxation undermines both its government’s legitimacy and its capacity to provide for its people.” Filing tax returns is not a mere administrative task, it is a declaration of participation in the collective project of national advancement.
In Nigeria’s context, this declaration carries weight. With the enactment of comprehensive tax reforms in recent years (including unified frameworks for tax administration and enforcement) authorities now possess broader statutory tools to ensure compliance and accountability. These measures, which include electronic filing platforms and stronger enforcement powers, have been framed as fair and equitable, targeting efficiency rather than arbitrariness.
Yet the success of these reforms depends heavily on citizens embracing their civic duties with sincerity. And this depends on mutual trust, the belief that paying taxes yields tangible benefits in infrastructure, education, healthcare, security and social services.
Voices From Experts: Fiscal Responsibility as a Public Ethic.
Tax law experts and economists, reflecting on the compliance push, have underscored a universal theme: taxation without transparency is inequity, but taxation with accountability is empowerment. When managed with fairness, a functional tax system can reduce dependency on volatile revenue sources, stabilise national budgets, and support long-term investment in human capital.
Professor Aisha Bello, a respected authority in fiscal policy, notes that “Tax compliance is not a burden; it is the foundation upon which social contracts are built. A citizen who honours tax obligations affirms the legitimacy of governance and demands better performance in return.”
Similarly, a leading tax scholar, Dr. Emeka Okon, argues that “The era when Nigerians could evade broader tax responsibilities simply because automatic deductions occur at source must end. For a modern economy, every eligible citizen must be part of the formal tax fold not as victims, but as stakeholders.”
These authoritative voices point to an unassailable truth: filing tax returns is both a legal requirement and a moral responsibility, an expression of citizenship in its fullest sense.
Challenges on the Ground: Compliance and Capacity.
While the rhetoric of compliance is compelling, the reality on the ground demands nuanced understanding. Many taxpayers (especially in the informal sector) lack meaningful access to digital platforms and resources for filing returns. For others, the fear of bureaucratic complexity and perceived punitive enforcement deters participation.
The government, for its part, has responded by promoting online systems and pledging greater taxpayer support. Tax authorities are increasingly engaging stakeholders to demystify filing processes, explain requirements and offer assistance. This mix of enforcement and facilitation is essential. As one seasoned revenue specialist observed: “The state cannot compel compliance through force alone; it must earn it through education, simplicity and fairness.”
The Broader Implication: A New Social Compact.
Ultimately, Nigeria’s renewed emphasis on tax return filing transcends administrative deadlines. It is an unequivocal declaration that national development is a shared responsibility, that citizens and state must engage in a transparent, accountable, and reciprocal relationship.
Tax compliance, therefore, becomes far more than a legal act; it becomes a moral claim on the nation’s future.
When citizens file their returns honestly, they affirm their stake in the nation’s destiny. When the government collects taxes transparently and deploys them effectively, it strengthens not only public services but civic trust itself.
In this sense, the deadlines proclaimed by Nigeria’s fiscal authorities mark not an end but a beginning; the beginning of a civic epoch in which accountability replaces apathy, participation replaces indifference and national purpose triumphs over fragmentation.
The road ahead will not be easy. But in demanding compliance, Nigeria is demanding more than tax returns. It is demanding commitment and that, ultimately, is the foundation on which nations are built.
Business
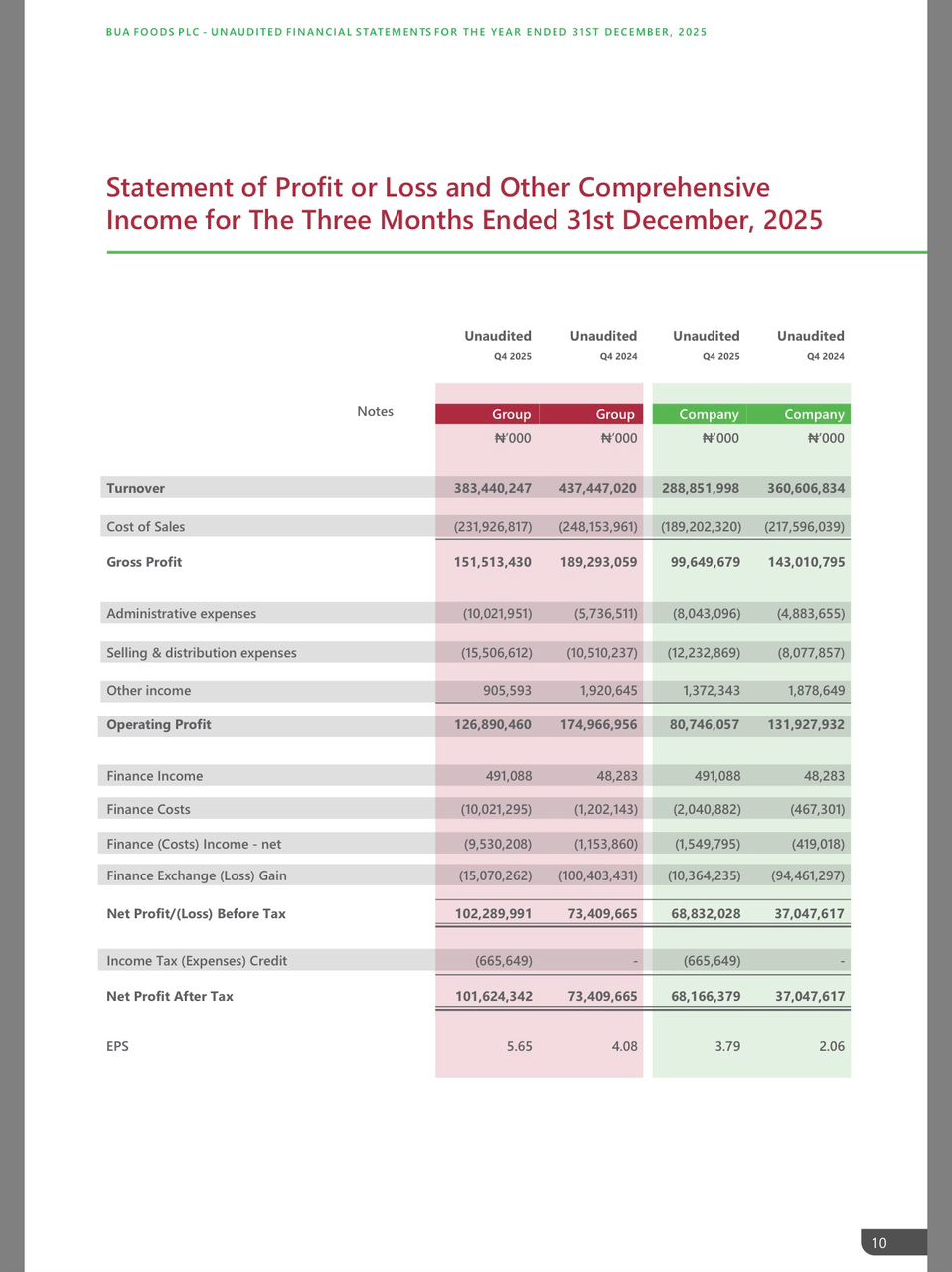
BUA Foods Records 91% Surge in Profit After Tax, Hits ₦508bn in 2025

BUA Foods Records 91% Surge in Profit After Tax, Hits ₦508bn in 2025
By femi Oyewale
Business
Adron Homes Unveils “Love for Love” Valentine Promo with Exciting Discounts, Luxury Gifts, and Travel Rewards

Adron Homes Unveils “Love for Love” Valentine Promo with Exciting Discounts, Luxury Gifts, and Travel Rewards
In celebration of the season of love, Adron Homes and Properties has announced the launch of its special Valentine campaign, “Love for Love” Promo, a customer-centric initiative designed to reward Nigerians who choose to express love through smart, lasting real estate investments.
The Love for Love Promo offers clients attractive discounts, flexible payment options, and an array of exclusive gift items, reinforcing Adron Homes’ commitment to making property ownership both rewarding and accessible. The campaign runs throughout the Valentine season and applies to the company’s wide portfolio of estates and housing projects strategically located across Nigeria.
Speaking on the promo, the company’s Managing Director, Mrs Adenike Ajobo, stated that the initiative is aimed at encouraging individuals and families to move beyond conventional Valentine gifts by investing in assets that secure their future. According to the company, love is best demonstrated through stability, legacy, and long-term value—principles that real estate ownership represents.
Under the promo structure, clients who make a payment of ₦100,000 receive cake, chocolates, and a bottle of wine, while those who pay ₦200,000 are rewarded with a Love Hamper. Payments of ₦500,000 attract a Love Hamper plus cake, and clients who pay ₦1,000,000 enjoy a choice of a Samsung phone or a Love Hamper with cake.
The rewards become increasingly premium as commitment grows. Clients who pay ₦5,000,000 receive either an iPad or an all-expenses-paid romantic getaway for a couple at one of Nigeria’s finest hotels, which includes two nights’ accommodation, special treats, and a Love Hamper. A payment of ₦10,000,000 comes with a choice of a Samsung Z Fold 7, three nights at a top-tier resort in Nigeria, or a full solar power installation.
For high-value investors, the Love for Love Promo delivers exceptional lifestyle experiences. Clients who pay ₦30,000,000 on land are rewarded with a three-night couple’s trip to Doha, Qatar, or South Africa, while purchasers of any Adron Homes house valued at ₦50,000,000 receive a double-door refrigerator.
The promo covers Adron Homes’ estates located in Lagos, Shimawa, Sagamu, Atan–Ota, Papalanto, Abeokuta, Ibadan, Osun, Ekiti, Abuja, Nasarawa, and Niger States, offering clients the opportunity to invest in fast-growing, strategically positioned communities nationwide.
Adron Homes reiterated that beyond the incentives, the campaign underscores the company’s strong reputation for secure land titles, affordable pricing, strategic locations, and a proven legacy in real estate development.
As Valentine’s Day approaches, Adron Homes encourages Nigerians at home and in the diaspora to take advantage of the Love for Love Promo to enjoy exceptional value, exclusive rewards, and the opportunity to build a future rooted in love, security, and prosperity.
-

 celebrity radar - gossips6 months ago
celebrity radar - gossips6 months agoWhy Babangida’s Hilltop Home Became Nigeria’s Political “Mecca”
-

 society6 months ago
society6 months agoPower is a Loan, Not a Possession: The Sacred Duty of Planting People
-

 Business6 months ago
Business6 months agoBatsumi Travel CEO Lisa Sebogodi Wins Prestigious Africa Travel 100 Women Award
-

 news6 months ago
news6 months agoTHE APPOINTMENT OF WASIU AYINDE BY THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AS AN AMBASSADOR SOUNDS EMBARRASSING











You must be logged in to post a comment Login