Business
All change!!! Nigeria is not an oil economy

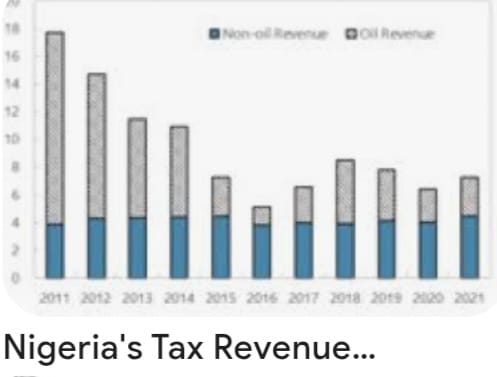
Descriptions of Nigeria’s economy often include such phrases as ‘Africa’s largest oil producer’ and ‘the oil rich African nation’ but oil economies are typically characterised by low population densities and abundant oil resources. Saudi Arabia with 10 million barrels of oil per day and 30 million people, Kuwait with 2.7 million barrels of oil per day and 4 million people and Qatar with 1.5 million barrels of oil per day and 2.5 million people are typical of such. These economies pursued an economic model that was built around a large government dependent almost entirely on oil revenue for funding. Such economies could afford to have low or in some cases no domestic revenue mobilisation, in the form of taxes. Tax to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) ratios of less than 10% against the OECD average of 34.6% could be justified especially in the era of high oil prices.
For over three decades, Nigeria pursued this model. But things are changing, with the election of President Muhammadu Buhari in 2015, who was propelled into office under the mantra of ‘change’. That clamour for change, in the areas of governance, security and economy, coincided with the collapse of global oil prices and a consequent huge deficit in government revenues. These circumstances provided the ingredients for an overhaul of the entire economic model. The first and rather numbing conclusion of that exercise was that Nigeria is not actually an ‘oil economy’. With just 2 million barrels of oil per day and over 180 million people, simple mathematics tells us that 90 Nigerians share a barrel of oil compared to 3 Saudis, 1.44 Kuwaitis and 1.69 Qataris. With oil at just 10% of GDP, Nigeria simply does not fit into the mould of the traditional oil economies.
Interestingly, even nations who did legitimately fit into this narrow mould of high oil revenues and low populations, are abandoning what is now considered to be a flawed model. Thus, the imperative for Nigeria was even more urgent. Nigeria recalibrated its target peer group from the oil economies to the ‘oil plus’ economies such as Mexico and Egypt. This new peer group have diversified economies and tax to GDP ratios of 20% and 16%, respectively, compared to Nigeria’s 6%. Consequently, the change mantra had to be urgently applied to revenue mobilisation.
Analysis of the data suggests that revenue mobilisation is potentially the master key to unlocking Nigeria’s huge growth potential by funding its ailing infrastructure including roads, power and rail. A cursory look at the effective tax rates paid by the huge multinational and local operators, as well as the data on illicit financial flows, indicates a pattern of systematic tax evasion at all levels. Recent statistics released by the Federal Ministry of Finance showed that Nigeria has just 14 million active tax payers from an economically active base of 70 million. Over 95% of these are salary earners in the formal sector, just 241 persons paid personal income taxes of N20m (US$65,573.77) in 2016. Taxing the high networth and Nigeria’s huge community of entrepreneurs constitutes a critical but yet attainable target. The statistics for corporate tax payment shows the debilitating effects of base erosion and profit shifting as well as abuse of an overly generous tax incentive and duty waiver system. The historical government apathy towards revenue mobilisation is one of the effects of the mistaken identity that saw Nigeria perceive itself as an oil economy. This Administration is determined to correct this identity crisis and all its concomitant effects.
In that spirit, we launched an ongoing and well received, tax amnesty, ‘The Voluntary Asset and Income Declaration Scheme’ (VAIDS) is affording a 9-month window for Nigerian tax payer’s, both corporate and individual, to regularise their tax status in exchange for a guarantee of no interest, penalties, tax investigation or further audit. This amnesty follows successful initiatives in a number of countries, where tax evasion is a problem, such as Indonesia, Argentina, South Africa and India. It has been programmed to end just as the Automatic Exchange of Information, which will provide Nigerian tax authorities with unprecedented levels of information on offshore assets, becomes effective.
The initial signs suggest that Nigerians are responding positively to the new revenue narrative. Despite the emergence from a recession, tax revenues are showing early signs of growth. VAT shows 18.97% year on year improvement. Over 800,000 companies, including some Government contractors, that have never paid taxes have already been identified and are being audited. This is an unprecedented initiative that entails cooperation between Federal and State Governments. The Federal Ministry of Finance has also commenced a database project that combines data from the various arms of government including bank records, property and company ownership, and customs records to create accurate profiles of those liable to pay taxes. The Ministry has also placed one of the world’s premier private investigation agencies on retainership to trace overseas assets.
Changing the Nigerian economic psyche is not an easy task. By its nature, tax mobilisation risks the popularity of any Government, but the present Administration understands that the short term lure of political expediency must give way to the long term best interests of Africa’s largest economy. Her energetic, young and growing population are deserving of the chance to experience a truly transformed, sustainable and growing economy.
Kemi Adeosun is Nigeria’s Minister of Finance
Business
Deadline of Compliance: Nigeria’s Urgent Call for Tax Return Filing

Deadline of Compliance: Nigeria’s Urgent Call for Tax Return Filing
By George Omagbemi Sylvester | Published by SaharaWeeklyNG.com
“Shift or Structural Demand? A Declaration of Civic Duty in a Nation at a Fiscal Crossroads.”
In the unfolding narrative of national development and economic reform, few instruments are as defining as tax compliance. For Nigeria, a nation perpetually grappling with revenue shortfalls, structural dependency on a single export commodity, and entrenched informal economic behaviour, the Federal Government’s recent clarification on tax return deadlines is not mere bureaucratic noise. It is a deliberate and inescapable declaration: the social contract between citizen and state must be honoured through transparent, lawful and timely tax reporting.
At its core, the government’s pronouncement is stark in its simplicity and radical in its implications. Federal authorities, speaking through the Chairman of the Presidential Committee on Fiscal Policy and Tax Reforms, Taiwo Oyedele, have made it unequivocally clear that every Nigerian, whether employer or individual taxpayer, must file annual tax returns under the law. This encompasses self-assessment filings by individuals that too many assumed ended once employers deducted pay-as-you-earn taxes from their salaries.
This is not an optional civic suggestion, it is mandatory, backed by statute, and tied to a broader vision of national fiscal responsibility. Citizens can no longer hide behind ignorance, apathy, or false assumptions. “Many people assume that if their employer deducts tax from their salaries, their obligations end there. That is wrong,” Oyedele warned, emphasizing that the obligation to file remains with the individual under both existing and newly reformed tax laws.
The Deadlines and the Reality They Reveal.
Across the federation, state and federal revenue authorities have reaffirmed statutory deadlines in pursuit of compliance. The Lagos State Internal Revenue Service, for instance, moved to extend its filing date for employer returns by a narrow window, reflecting the reality that compliance often lags behind legal timelines. The extension was intended not as leniency, but as a pragmatic effort to allow accurate and complete submissions, underscoring that true compliance rises above mere mechanical ticking of a box.
At the federal level, Oyedele’s intervention was even more fundamental. He reminded Nigerians that annual tax returns for the preceding year must be filed in good faith, with integrity and in respect of the law. This applies regardless of income level including low-income earners who have historically believed that they are outside the tax net. “All of us must file our returns, including those earning low income,” he stated.
Herein lies one of the most challenging truths of contemporary Nigerian governance: widespread tax non-compliance is not just a technical breach of law, it is a deep cultural and structural issue that reflects decades of mistrust between citizens and the state.
The Root of the Problem: Non-Compliance as a Symptom.
Nigeria’s tax culture has long been under scrutiny. Public discourse and economic analysis consistently show that a significant majority of eligible taxpayers do not file annual returns. Oyedele highlighted that even in states widely regarded as tax administration leaders, compliance remains strikingly low, often below five percent.
This widespread non-compliance stems from multiple sources:
A long history of weak tax administration systems, where enforcement was inconsistent and penalties were rarely applied.
A perception that public services do not reflect the taxes collected, eroding the citizenry’s belief in reciprocity.
An informal economy where income often goes unrecorded, making filing seem irrelevant or impossible to many.
Lack of awareness, with many Nigerians genuinely believing that tax liability ends with employer deductions.
The government’s renewed push for compliance directly challenges these perceptions. It signals a shift from voluntary or lax compliance to structured accountability, a stance that aligns with best practices in modern public finance.
Why This Matters: Beyond Deadlines.
At its most profound level, the insistence on tax return filings is about nation-building and shared responsibility.
Scholars of public finance universally agree that a robust tax system is the backbone of sustainable development. As the eminent economist Dr. Joseph E. Stiglitz has observed, “A society that cannot mobilize its own resources through fair taxation undermines both its government’s legitimacy and its capacity to provide for its people.” Filing tax returns is not a mere administrative task, it is a declaration of participation in the collective project of national advancement.
In Nigeria’s context, this declaration carries weight. With the enactment of comprehensive tax reforms in recent years (including unified frameworks for tax administration and enforcement) authorities now possess broader statutory tools to ensure compliance and accountability. These measures, which include electronic filing platforms and stronger enforcement powers, have been framed as fair and equitable, targeting efficiency rather than arbitrariness.
Yet the success of these reforms depends heavily on citizens embracing their civic duties with sincerity. And this depends on mutual trust, the belief that paying taxes yields tangible benefits in infrastructure, education, healthcare, security and social services.
Voices From Experts: Fiscal Responsibility as a Public Ethic.
Tax law experts and economists, reflecting on the compliance push, have underscored a universal theme: taxation without transparency is inequity, but taxation with accountability is empowerment. When managed with fairness, a functional tax system can reduce dependency on volatile revenue sources, stabilise national budgets, and support long-term investment in human capital.
Professor Aisha Bello, a respected authority in fiscal policy, notes that “Tax compliance is not a burden; it is the foundation upon which social contracts are built. A citizen who honours tax obligations affirms the legitimacy of governance and demands better performance in return.”
Similarly, a leading tax scholar, Dr. Emeka Okon, argues that “The era when Nigerians could evade broader tax responsibilities simply because automatic deductions occur at source must end. For a modern economy, every eligible citizen must be part of the formal tax fold not as victims, but as stakeholders.”
These authoritative voices point to an unassailable truth: filing tax returns is both a legal requirement and a moral responsibility, an expression of citizenship in its fullest sense.
Challenges on the Ground: Compliance and Capacity.
While the rhetoric of compliance is compelling, the reality on the ground demands nuanced understanding. Many taxpayers (especially in the informal sector) lack meaningful access to digital platforms and resources for filing returns. For others, the fear of bureaucratic complexity and perceived punitive enforcement deters participation.
The government, for its part, has responded by promoting online systems and pledging greater taxpayer support. Tax authorities are increasingly engaging stakeholders to demystify filing processes, explain requirements and offer assistance. This mix of enforcement and facilitation is essential. As one seasoned revenue specialist observed: “The state cannot compel compliance through force alone; it must earn it through education, simplicity and fairness.”
The Broader Implication: A New Social Compact.
Ultimately, Nigeria’s renewed emphasis on tax return filing transcends administrative deadlines. It is an unequivocal declaration that national development is a shared responsibility, that citizens and state must engage in a transparent, accountable, and reciprocal relationship.
Tax compliance, therefore, becomes far more than a legal act; it becomes a moral claim on the nation’s future.
When citizens file their returns honestly, they affirm their stake in the nation’s destiny. When the government collects taxes transparently and deploys them effectively, it strengthens not only public services but civic trust itself.
In this sense, the deadlines proclaimed by Nigeria’s fiscal authorities mark not an end but a beginning; the beginning of a civic epoch in which accountability replaces apathy, participation replaces indifference and national purpose triumphs over fragmentation.
The road ahead will not be easy. But in demanding compliance, Nigeria is demanding more than tax returns. It is demanding commitment and that, ultimately, is the foundation on which nations are built.
Business
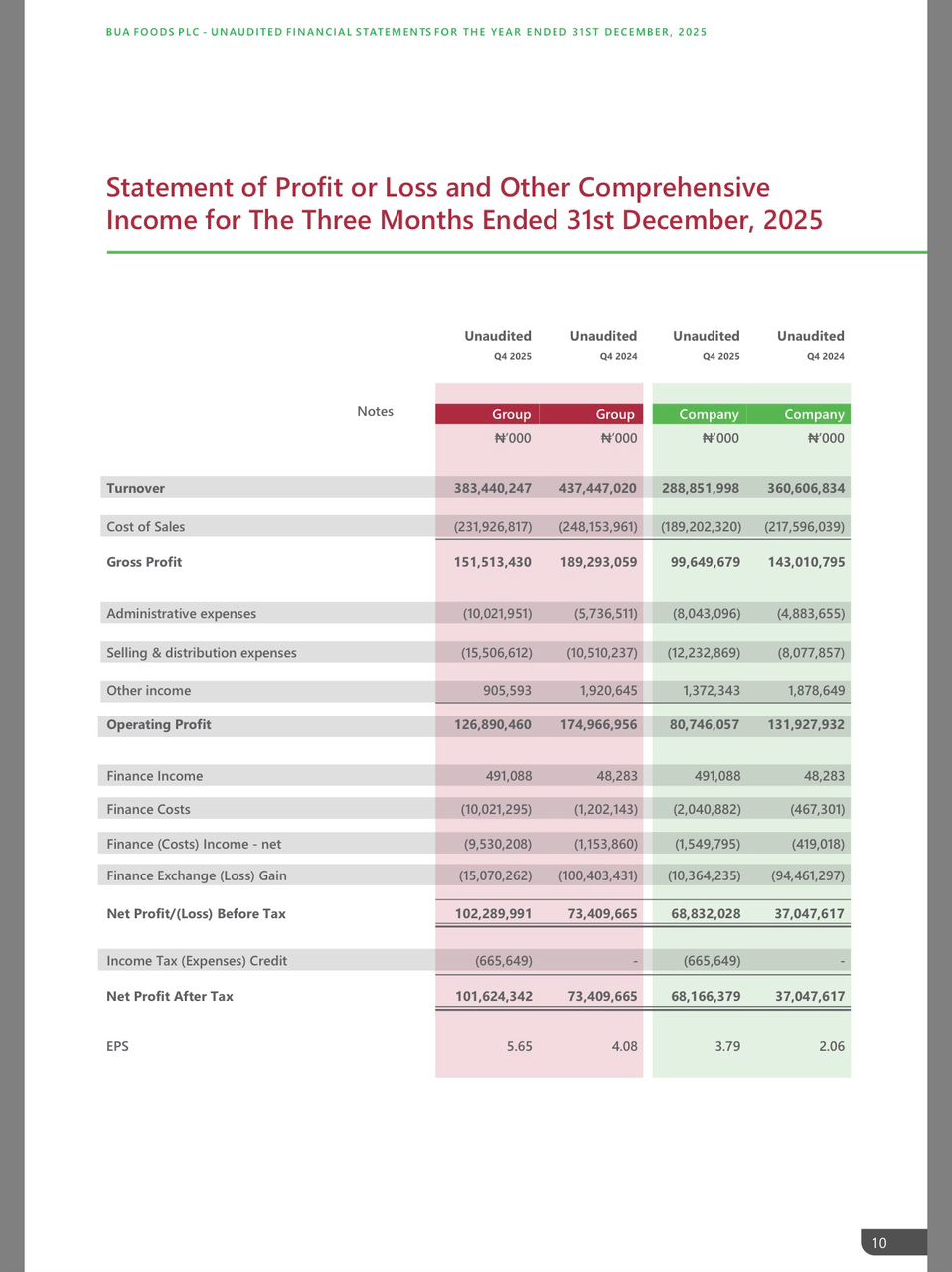
BUA Foods Records 91% Surge in Profit After Tax, Hits ₦508bn in 2025

BUA Foods Records 91% Surge in Profit After Tax, Hits ₦508bn in 2025
By femi Oyewale
Business
Adron Homes Unveils “Love for Love” Valentine Promo with Exciting Discounts, Luxury Gifts, and Travel Rewards

Adron Homes Unveils “Love for Love” Valentine Promo with Exciting Discounts, Luxury Gifts, and Travel Rewards
In celebration of the season of love, Adron Homes and Properties has announced the launch of its special Valentine campaign, “Love for Love” Promo, a customer-centric initiative designed to reward Nigerians who choose to express love through smart, lasting real estate investments.
The Love for Love Promo offers clients attractive discounts, flexible payment options, and an array of exclusive gift items, reinforcing Adron Homes’ commitment to making property ownership both rewarding and accessible. The campaign runs throughout the Valentine season and applies to the company’s wide portfolio of estates and housing projects strategically located across Nigeria.
Speaking on the promo, the company’s Managing Director, Mrs Adenike Ajobo, stated that the initiative is aimed at encouraging individuals and families to move beyond conventional Valentine gifts by investing in assets that secure their future. According to the company, love is best demonstrated through stability, legacy, and long-term value—principles that real estate ownership represents.
Under the promo structure, clients who make a payment of ₦100,000 receive cake, chocolates, and a bottle of wine, while those who pay ₦200,000 are rewarded with a Love Hamper. Payments of ₦500,000 attract a Love Hamper plus cake, and clients who pay ₦1,000,000 enjoy a choice of a Samsung phone or a Love Hamper with cake.
The rewards become increasingly premium as commitment grows. Clients who pay ₦5,000,000 receive either an iPad or an all-expenses-paid romantic getaway for a couple at one of Nigeria’s finest hotels, which includes two nights’ accommodation, special treats, and a Love Hamper. A payment of ₦10,000,000 comes with a choice of a Samsung Z Fold 7, three nights at a top-tier resort in Nigeria, or a full solar power installation.
For high-value investors, the Love for Love Promo delivers exceptional lifestyle experiences. Clients who pay ₦30,000,000 on land are rewarded with a three-night couple’s trip to Doha, Qatar, or South Africa, while purchasers of any Adron Homes house valued at ₦50,000,000 receive a double-door refrigerator.
The promo covers Adron Homes’ estates located in Lagos, Shimawa, Sagamu, Atan–Ota, Papalanto, Abeokuta, Ibadan, Osun, Ekiti, Abuja, Nasarawa, and Niger States, offering clients the opportunity to invest in fast-growing, strategically positioned communities nationwide.
Adron Homes reiterated that beyond the incentives, the campaign underscores the company’s strong reputation for secure land titles, affordable pricing, strategic locations, and a proven legacy in real estate development.
As Valentine’s Day approaches, Adron Homes encourages Nigerians at home and in the diaspora to take advantage of the Love for Love Promo to enjoy exceptional value, exclusive rewards, and the opportunity to build a future rooted in love, security, and prosperity.
-

 celebrity radar - gossips6 months ago
celebrity radar - gossips6 months agoWhy Babangida’s Hilltop Home Became Nigeria’s Political “Mecca”
-

 society6 months ago
society6 months agoPower is a Loan, Not a Possession: The Sacred Duty of Planting People
-

 Business6 months ago
Business6 months agoBatsumi Travel CEO Lisa Sebogodi Wins Prestigious Africa Travel 100 Women Award
-

 news6 months ago
news6 months agoTHE APPOINTMENT OF WASIU AYINDE BY THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AS AN AMBASSADOR SOUNDS EMBARRASSING











You must be logged in to post a comment Login