society
Legal Status of Nullified Order of Arrest

Legal Status of Nullified Order of Arrest
The vacation of warrants of arrest, search and commitment to prison on remand against Dr. Akintoye Akindele, the Managing Director/Chief Executive Officer of Duport Midstream Company Limited in suit no. CMC/MG/CR/17S/2023 by a Chief Magistrate Court in Nasarawa State sitting at Mararara Gurku is of topical interest.
The Inspector General of Police was the complainant in the suit. By vacating its own order, the court has provided further proof as to the robustness of the judicial system to resist attempts at pressing it into service as a tool for impunity.
There are instances where the police may arrest a person in circumstances where the arrest ought not have been made in the first instance. Such arrests may be nullified by the same court or by courts of equal jurisdiction.
The question which arises is the legal status of such nullified orders of arrest. The grounds for nullification may include defects in the jurisdiction of the court, non- disclosure and/or suppression of crucial information by the police, et cetera.
This publication seeks to lay to rest the status of the unlawful arrest by the police of such a person.
Introduction
This opinion addresses a pivotal issue:
Can a Magistrate Court in Nasarawa State, for example, lawfully issue warrants and committal orders on the bases of untrue/concealed information from the police concerning alleged offenses committed beyond the court’s jurisdiction?
And, where such orders of arrest are made but subsequently quashed, what is the legal status of the quashed order of arrest?
Jurisdictional authority of Magistrate Courts in Nasarawa State.
The bedrock of the authority of Magistrate Courts in Nasarawa State to issue arrest and search warrants is rooted in the Administration of Criminal Justice Law (ACJL) of Nasarawa State.
This legal framework, meticulously detailed in Sections 35, 36, 143, and 144 of the ACJL Nasarawa State, provides a precise avenue through which these courts can empower law enforcement agencies to apprehend suspects and secure crucial evidence.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the limitations stemming from the territorial jurisdiction of these courts.
For instance, the jurisdictional scope of the Chief Magistrate’s Court in Maraba-Gurku, Nasarawa State, is explicitly defined within the official gazette.
Legal Analysis of the Issue
The key issue for determination is as follows: Do Magistrate Courts possess the capability to extend their arm of authority to issue warrants for offences that transpire beyond the territorial confines of their jurisdiction? This question emanates from the bedrock of Nigerian legal principle on the doctrine of territorial jurisdiction.
The landmark case of REX V. SHODIPO 12 WACA 374 resonates adequately with the geographical limitations on jurisdiction.
Territorial Constraints on the Jurisdiction of Magistrate Courts
It is crucial to acknowledge the limitations that govern the jurisdiction of a Magistrate Court in criminal cases.
This jurisdiction is inherently restricted to the geographical scope of its corresponding state, often defined by delineations within magisterial districts where applicable.
In REX v. SHODIPO 12 WACA 374, the facts, circumstances, and rulings of the West African Court of Appeal vividly demonstrate the profound consequences of errors in jurisdiction.
In this case, an appellant arrested in Lagos for a crime committed in Ijoko, situated within the Abeokuta Magisterial District, triggered a preliminary inquiry that resulted in the appellant’s trial in the Lagos Division of the then Supreme Court.
The charge primarily revolved around fraudulent false accounting, as stipulated under Section 6 of the Criminal Code. Central to the appellant’s argument was Section 64 of the Criminal Procedure Ordinance, contending that the preliminary inquiry should have transpired within the Abeokuta Magisterial District, rendering the Lagos Magistrate’s proceedings null. The West African Court of Appeal concurred, establishing that the Lagos Magistrate lacked jurisdiction over the preliminary inquiry. Consequently, all ensuing proceedings, including the Supreme Court trial, were null and void. This fundamental principle of criminal justice administration is further enriched by the 2017 reported case of MATHEW V. THE STATE (2017) LPELR-44072(CA), wherein the Court of Appeal, per FATIMA OMORO AKINBAMI, JCA underscored the essence of jurisdiction as the bedrock of adjudication: “Jurisdiction defines the power of the Court to inquire into facts, apply the law, make decisions and declare judgment. The Constitution and statutes which set up the Courts cloak them with powers and jurisdiction of adjudication which are basically substantive and procedural. Thus, where ingredients of an offence occur outside the territorial jurisdiction of the Court asked to adjudicate over the matter, such a Court will not assume jurisdiction over the offence for apparent lack of jurisdiction.” On this score, it is our opinion and as supported by the order voiding the arrest, that the magistrate, ab initio, lacked the jurisdiction to issue the warrant of arrest as none of the alleged elements of the case occurred within his jurisdiction in Nassarawa State.
Non-Disclosure and Suppression of Facts
The issue of non-disclosure of material facts by the Police to the Magistrate is fatal to the legality of the original warrant of arrest. Complainants in criminal litigation, bear the obligation of offering forthright disclosure of facts before the court.
Where complainants, including the Police hide, distort and or obscure the facts from the Magistrate in order to secure a warrant by such deceit, there are legal consequences for such underhand tactics.
In the case of non- disclosure leading to a remand order, the complainant’s failure to disclose pivotal facts—such as the residence and business activities of both the nominal complainant and the defendant(s) casts a shadow of doubt on the veracity and legality of the proceedings.
This concealment assumes the character of a foundational flaw, jeopardizing the structural integrity of the legal process, and ultimately rendering all acts, proceedings, and orders of the court a nullity.
As upheld by the Supreme Court, per Dr. I.T. Muhammed, JSC in DINGYADI &? ANOR V. INEC & 2 ORS (No. 2) (2010) 18 NWLR (PT. 1224), where it stated:
“The law regarding the position of any judgment or order of court which is a nullity for any reason whatsoever, is that the court in its inherent jurisdiction is entitled ex debito justitiae to have that judgment or order set aside on application of an affected or aggrieved party or even suo motu by the court itself.”
The Court’s Authority to Rectify Its Own Errors
In the final analysis, the law is clear that the courts have the inherent jurisdiction to nullify warrants which it had earlier issued in error.
The case of INTERMARKET NIG. V. ADEROUNMU (1998) 12 NWLR (PT. 576) 131 AT 145 stands as a testament to the court’s ability to undo orders erected on shaky foundations. Furthermore, the court’s capacity to set aside its own decisions upon the emergence of concealed material facts is substantiated in cases like ANAEKWE V. MASHASHA (2001) 12 NWLR (PT. 726) 70 AT 91 PARAS D-F and UNIVERSAL TRUST BANK LIMITED & ORS V. DOBMATSCH PHARMACY NIGERIA LIMITED [2008] 156 LRCN 197 AT 216 ZJJ TO 217AK. Embedded within legal doctrine is the principle that a court, upon recognizing concealed material facts that would have significantly influenced its decision, possesses the prerogative to overturn the earlier order.
The potency of concealed facts in corroding the legitimacy of proceedings is underscored by the case of BELLO OGUNDELE & ANOR V. SHITTU AGIRI & ANOR (2009) 12 SC PT 1, 135.
In this pivotal case, the court rendered the judgment of the lower court null and void due to the concealment of crucial facts.
In the words of the court: “The respondents falsely misrepresented the proceedings of Ila Native Court in Suit No HOS/1/79 by concealing the final judgment of that Court, which led to the judgment delivered by the Honorable Justice S.A Oloko in 1981. Consequently, the Judgment of the Lower Court is hereby set aside.”
Similarly, in ANAEKWE V. MASHASHA (2001) 12 NWLR (PT.726) 70, the court observed that: “This court has always the jurisdiction to set aside its own null judgment, or decision… See Chime V. Ude (1996) 7 NWLR (pt. 461) 379 at 438. Where it was held that if the court had acted under misapprehension of facts, the court had the power to set aside its own decision…”
Thus, by implication, when a court corrects its errors by setting aside a judgment or orders made, it is interpreted that such proceedings, judgment, or orders never existed– a total reversal to the circumstances prior to the order made.
In IBRAHIM v. OJONYE (2011) LPELR-3737(CA), the court held that: “It is a cardinal principle of law as submitted by the Appellant’s Counsel, that a judgment remains valid until set aside. However, it is worthy to note that a judgment can be set aside whether it has been executed upon or not. By setting aside a judgment, the said judgment becomes ineffectual and nugatory that nothing can cure it. In that circumstance, both the Court and the parties would revert to or return to their former position before the said judgment was delivered…”
Conclusion
It is evident that when a magistrate court issues orders founded upon concealed facts and pertains to offenses occurring beyond its jurisdiction, the entirety of the proceedings is rendered null and void.
Where such a nullification order has been made, the legal status of the nullified order is that it never existed in the first instance.
The subsequent nullification of such orders underscores the fact that, in the eyes of the law, those orders were as if they were never made.
Therefore, the very act of a Magistrate Court issuing these orders and warrants stands fundamentally illegal, and devoid of legal validity from its inception. As to the defendant, the pathway to seek redress from the complainant, in this case, the Inspector General of Police, for substantial reputational damages and financial losses suffered as a fallout of his detention, is wide open. Depending on how the case plays out in court, it may become a reference point for raising standards of police transparency when seeking a warrant.
Prof. Ikechi Mgbeoji is of Blackfriars LLP, a law firm in Lagos.
society
Banwo Questions Bwala’s Credibility After Al Jazeera Interview

Banwo Questions Bwala’s Credibility After Al Jazeera Interview
Public commentator, Dr. Ope Banwo, has criticised Daniel Bwala, the Presidential Spokesperson on Policy Communication for President Bola Ahmed Tinubu, following a contentious interview on Al Jazeera, describing the appearance as damaging to the credibility of Nigeria’s public communication.
Bwala had appeared on a programme hosted by journalist Mehdi Hasan, where he faced a series of questions about past statements attributed to him. During the exchange, Hasan presented video clips of previous remarks by the government spokesman and asked him to reconcile them with his responses during the interview.
The exchange, which has since circulated widely online, drew attention after Bwala appeared to dispute statements that were subsequently played back during the programme.
Reacting to the development, Banwo said the episode reflected poorly on Nigeria’s representation on international media platforms.
According to him, the availability of digital records and online archives means public officials must be prepared to defend their past statements whenever they appear on global television.
“In the era of instant fact-checking, any public figure going on international television must assume that every previous statement can be easily retrieved,” Banwo said.
He added that the controversy surrounding the interview was particularly troubling because the contradictions presented during the programme were supported with video evidence.
Banwo noted that while political interviews can be confrontational, government representatives should expect tough questioning when appearing before international audiences.
The founder of Naija Lives Matters also expressed concern over Bwala’s reaction during the interview, especially his claim that he was not informed he would be required to defend his personal record.
“A government spokesman should never be surprised by questions about his own public statements,” Banwo said.
During the programme, Bwala also responded to criticism of Nigeria’s governance challenges by arguing that similar problems exist in other parts of the world.
However, Banwo argued that such comparisons do not address the specific issues raised about Nigeria.
According to him, the episode should serve as a reminder of the importance of preparation and credibility when Nigerian officials appear before international media platforms.
The interview has continued to generate reactions across social media and political commentary circles, with observers debating both the conduct of the interview and the implications for Nigeria’s global image.
society
THE IMPERIAL GOLD COIN OF THE UNITED KINGDOM OF ATLANTIS UNVEILED AS SYMBOL OF SOVEREIGNTY AND HERITAGE

THE IMPERIAL GOLD COIN OF THE UNITED KINGDOM OF ATLANTIS UNVEILED AS SYMBOL OF SOVEREIGNTY AND HERITAGE
_[Atlantis City, United Kingdom of Atlantis – March 2026]_ – The United Kingdom of Atlantis proudly announces the introduction of its *Imperial Gold Coin*, a magnificent emblem of sovereignty, authority, and imperial heritage. The exquisite gold coin has been crafted to represent the nation’s regal tradition, economic strength, and the visionary leadership of its monarch.
The centerpiece of the coin features the dignified portrait of *His Imperial Majesty, Professor Solomon Wining*, depicted in full royal regalia. Crowned with a majestic golden crown and adorned with intricately crafted ornaments, the portrait embodies honor, wisdom, and noble leadership befitting a sovereign ruler. The depiction celebrates the monarch’s reign, which is associated with wisdom, development, and the pursuit of justice.
The golden coin itself signifies *prosperity, stability, and the enduring legacy* of the Atlantis Kingdom. Gold, historically a universal symbol of power, wealth, and permanence, reflects the strength and vision of the kingdom’s leadership and its aspirations for lasting greatness.
Encircling the royal portrait is the carefully engraved inscription *“United Kingdom of Atlantis”*, reinforcing the state’s identity any the authority of its sovereign ruler. The lower rim of the coin prominently displays the name *Solomon Wining*, commemorating the monarch whose leadership is linked to noble governance and national advancement.
The phrase *“Gold Coin”* highlights not only the currency’s intrinsic value but also its symbolic significance as a representation of the kingdom’s economic structure and royal treasury. Beyond its aesthetic elegance, the coin serves as a *mark of sovereignty*, a seal of authority, and a reminder of the royal institution governing the United Kingdom of Atlantis.
The Imperial Gold Coin represents:
– *Unity* among citizens,
– *Loyalty* to the crown,
– A vision of a kingdom built upon *justice, prosperity, and noble leadership*.
Every detail—from the engraved crown to the polished golden surface—makes the coin a timeless emblem of imperial prestige and national pride. It stands as both a symbol of wealth and a monument to the legacy of royal leadership, reminding all who behold it of the enduring power and majesty of the United Kingdom of Atlantis.
The United Kingdom of Atlantis is a sovereign nation dedicated to upholding traditions of regal governance, cultural heritage, and economic prosperity, guided by the wisdom of its imperial leadership.
_Notes to Editors_:
The Imperial Gold Coin is intended for commemorative and symbolic purposes, representing the nation’s imperial heritage and royal authority.
society
Ajadi Visits Ibadan Chief Imam, Receives Blessings
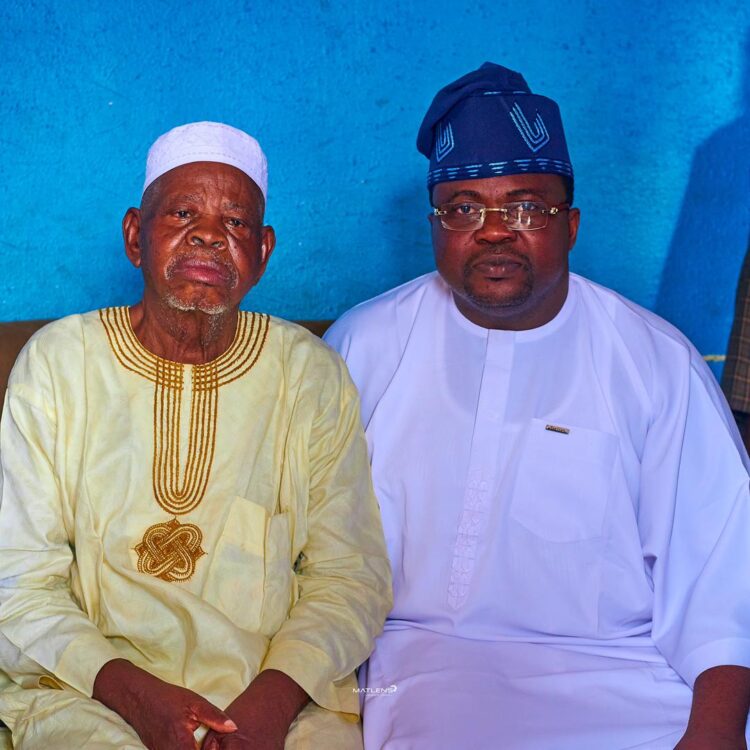
Ajadi Visits Ibadan Chief Imam, Receives Blessings
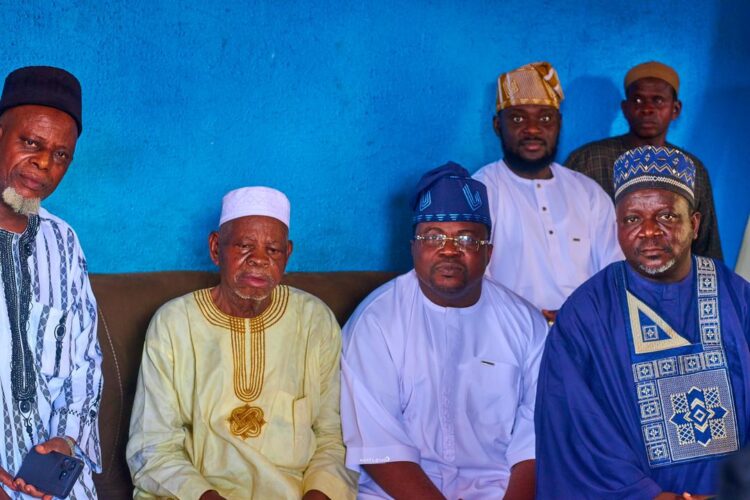
The leading gubernatorial aspirant in Oyo State on the platform of the Peoples Democratic Party (PDP), Ambassador Olufemi Ajadi Oguntoyinbo, on Wednesday paid a courtesy visit to the Grand Chief Imam of Ibadanland, Sheikh Imam Abdul Ganiy Abubakir Agbotomokekere, at his Oja’ba residence in Ibadan, where discussions centred on leadership, integrity, and the role of prayers in governance.
Ajadi, who described the revered Islamic cleric as a spiritual pillar in Oyo State, said his visit was to seek prayers and wise counsel as he continues consultations ahead of the 2027 governorship race.
While addressing the Chief Imam, Ajadi commended his consistent prayers for Ibadanland, Oyo State and Nigeria, noting that religious leaders remain critical stakeholders in nation building.
“I have come to seek your prayers and spiritual blessings because of your important role in promoting peace, unity and moral guidance in our society,” Ajadi said.
“I also want to appreciate your continuous prayers for the progress of Ibadanland, Oyo State and Nigeria as a whole. My prayer is that Almighty Allah will continue to grant you sound health and long life to witness many more Ramadan seasons on earth.”
Speaking further, the PDP gubernatorial aspirant emphasised the need for leadership driven by compassion, fairness and accountability, stressing that his political aspiration is rooted in service to the people.
“My ambition is not just about occupying an office but about serving the people with sincerity and fear of God. We must continue to encourage politics that will bring development and improve the welfare of our people,” he added.
While speaking with journalists after the visit, Ajadi also assured the people of Oyo State and Nigerians at large that the internal crisis and political tensions within the Peoples Democratic Party (PDP) have been brought under control by the grace of God. He expressed optimism that the party would emerge victorious in all elective positions in the 2027 general elections.
In his response, Sheikh Agbotomokekere advised the governorship hopeful to remain focused on the principles of good governance, warning against corrupt practices often associated with politics.
The respected Islamic scholar noted that while politics is practised differently by individuals, only leaders with integrity and fear of God can truly deliver the dividends of democracy.
“Politics is practised by different kinds of people. Some play politics in a corrupt way, while others practise it with sincerity. My prayer is that you will be among those who will practise democracy in the right way if you become governor,” the Chief Imam said.
He reminded the aspirant that human ambition can only be fulfilled by divine approval, stressing that ultimate power belongs to God.
“Whoever is seeking a position should know that only Allah can make such an ambition come true. Whether a person becomes famous or remains unknown is also by the will of Allah,” he said.
Offering prayers for the politician, the cleric added: “Many people may be struggling for a position meant for one person, and it is only God who knows the rightful person. I pray that Almighty Allah will make you the chosen one among all the contenders.”
Using a football analogy to further illustrate his point, the cleric advised Ajadi to be wary of political distractions and misleading influences.
“On the football field, sometimes spectators believe they understand the game more than the players themselves. I pray that you will not be misled by so-called political gurus and that God will guide your steps aright,” he said.
Sheikh Agbotomokekere, the 18th Chief Imam of Ibadanland, is widely respected across South-Western Nigeria for his scholarship, spiritual leadership and advocacy for peaceful coexistence among religious and political groups.
Observers say the visit forms part of Ajadi’s ongoing consultations with key stakeholders, traditional rulers and religious leaders as political activities gradually gather momentum ahead of the next electoral cycle in Oyo State.
The cleric offered special prayers for peace in Oyo State, successful leadership, and continued unity among the people despite political and religious differences.
-

 society6 months ago
society6 months agoReligion: Africa’s Oldest Weapon of Enslavement and the Forgotten Truth
-

 news3 months ago
news3 months agoWHO REALLY OWNS MONIEPOINT? The $290 Million Deal That Sold Nigeria’s Top Fintech to Foreign Interests
-

 society6 months ago
society6 months ago“You Are Never Without Help” – Pastor Gebhardt Berndt Inspires Hope Through Empower Church (Video)
-

 Business7 months ago
Business7 months agoGTCO increases GTBank’s Paid-Up Capital to ₦504 Billion







