Business
Dangote: The Monopoly We All Need By Mary Odoma

Dangote: The Monopoly We All Need
By Mary Odoma
There seems to be a huge partition between Nigerian industrialist Alhaji Aliko Dangote and other Nigerian economy drivers. His visionary gait and purposefulness are fixated on recreating the essentials required to prop up the depleting economic fortune of Nigeria amidst contending voices.
Since 1977, when he ventured into business, trading in agricultural commodities and engaging in business supplies such as sugar and cement, Alhaji Aliko Dangote has never looked back. In 1981, he incorporated his numerous businesses, which eventually became a conglomerate. Today, the Dangote Group of Companies is a household name in Nigeria and beyond.
The holding company’s interest became so massive that its positive economic impact within Nigeria and sub-Saharan Africa became profound, edging out numerous foreign products from the West African domestic market. A strong advocate of industrialization, Alhaji Dangote believes that dependence on the importation of finished products to Africa simply translates to the importation of poverty and the exportation of jobs.
So, when the idea of the Dangote refinery was first announced in 2013, it was indeed heartwarming news to Nigerians. Although construction of the world’s biggest single-train refinery began in 2017, there were prospects that its completion would end Nigeria’s energy crises and reliance on fuel importation.
In 2013, the refinery project was estimated to cost the Dangote Group a whopping $9 billion. However, by the time construction work began in 2017, the cost had risen to about $15 billion. Despite this disparity in estimated cost, the Dangote Group went ahead with the construction work, which was estimated to be completed in 2019. Regrettably, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the completion date was further shifted, and the date for commissioning was scheduled for the first half of 2021, but the 2021 date could not work due to unforeseen circumstances.
In all, at commissioning in the second quarter of 2023, precisely on May 23, construction of the refinery had gulped nearly $20 billion. It is an understatement to assert that building an efficient oil refinery facility has been at the heart of the debate over energy, forex, and fiscal policies in Nigeria for the last 50 years. This is because Nigeria’s four government-owned refineries, with a cumulative capacity of about 445,000 barrels per day (bpd), have been moribund for decades.
This meant that Nigeria exports its oil in crude form and imports refined oil with scarce foreign exchange. The attendant implication, therefore, was the emergence of the fuel subsidy regime, which was bad for Nigeria’s economic prospects. The regime led to the worsening state of the nation’s budget deficits as Nigeria’s debt profile increased with gloomy economic growth indices.
Against this background, several analysts drew up conclusions that the backlash received by the Dangote Group for daring to embark on such a massive project was an attempt to monopolise the economic benefits of the oil sector. Those naysayers had labelled the magnificent single-train refinery complex as a needless monopoly.
They orchestrated attacks and employed subversive antics just because they felt that the coming onstream of the Dangote multi-billion-dollar single-train refinery complex, the largest in the world, would finally put an end to their sordid business activities, which have held the nation’s economic lifeline hostage for more than five decades.
These few individuals are the fuel subsidy racketeers who have had their hands soiled in humongous scale corruption, diversion of the nation’s resources from critical sectors of the economy, as well as sharing profits of such loots amongst themselves and cronies in an inequitable manner.
Good enough, the multi-million-dollar Dangote refinery is here to bring the Nigerian dream to fruition. The refinery would meet 100% of all refined products required in Nigeria and a surplus for export. Though designed to process Nigerian crude, the refinery can also process most other African crude grades as well as Middle Eastern Arab light and even US Light.
The target is that, with a capacity of 650,000 barrels of crude per day, 450,000 bpd will be dedicated to meeting Nigeria’s domestic requirement. This means a total rejuvenation of the nation’s economy. Although the refinery has started with the production of diesel and aviation fuel, the sorting news is that the waiting game is over, the jinx has been broken.
It is instructive to admit that the import of the Dangote refinery coming on stream at this time is beyond the potential positive changes Nigeria’s economic indicators would witness in a few months. The positive impact of the multi-billion-dollar refinery would ultimately reflect directly on Nigeria’s foreign exchange reserves by reducing the pressure on the nation’s balance of payment.
This means that under President Tinubu, Nigeria would save trillions of naira and billions of dollars. For instance, between 2022 to 2023 alone, Nigeria spent over $70 billion on the importation of petroleum products, fertilizer, and petrochemicals, according to Africa Economy Digest.
Whatever the perception may be, Nigeria is at a crossroads. The country’s gloomy economic indicators that have remained a burden over the years are set to fizzle out for the better as the massive Dangote single-train world’s largest refinery debuts in the oil and gas sector.
Unfortunately, the reactive response of subsidy racketeers almost swayed the government’s decision on policies concerning the sale of Nigerian crude to local refineries, but thank goodness, the tide has assumed a positive dimension with recent impressive turns of events.
The evolving trend in the petroleum sector is what Nigeria requires to move forward; significantly, the feared Dangote refinery monopoly is what Nigeria as a nation requires now to thrive economically. This assertion is made more profound because the multi-billion-dollar refinery would, aside from saving the naira, make available vital raw materials of a wide range for manufacturers in the plastic, pharmaceuticals, food, beverages, construction, and other industries with massive job opportunities.
Candidly, the Dangote refinery is an ambitious move that has highlighted Nigeria’s potential for economic self-reliance. The $20 billion single-train Dangote refinery was envisioned to revolutionize the Nigerian oil and gas sector. Expectedly, the journey has not been without the usual criticism, with people raising questions about the rationale behind embarking on such a massive project in a developing and tottering economy.
The aim was basically to demonize the good intentions of the Dangote Group and its vision for Nigeria’s future. The hurting criticism was targeted at labelling the Dangote Group as shrewd capitalists whose target is to monopolize the Nigerian oil-based economy and beyond. However, the Dangote Group’s objective is clear; its intentions are not ambiguous. It is rather a blessing to the nation with the sole aim of reducing Nigeria’s dependence on the importation of refined petroleum products.
By refining petroleum products domestically, the Dangote refinery aims to enhance energy sufficiency, creating jobs, and spurring economic growth. Dangote refinery stands as a testament to Nigeria’s industrial ambitions and the complex interplay of business strategy, economic policy, and national interest.
No doubt, the Dangote refinery would, in no small measure, offer dividends similar to those from the Nigerian Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) investment, which has consistently provided returns despite initial scepticism. Furthermore, aside from boosting economic activities in the country, there will be revenue accruing to the government through taxes, royalties, and levies as the refinery comes on stream.
At least 144 products out of about 6000 products will be extracted in the process of refining petroleum. This means the value chain of refined petroleum products is very long and can stimulate a lot of businesses. Also, the multi-billion-dollar refinery would serve as a foreign exchange earner.
Industry experts projected that Nigeria could spend up to $30 billion in one year if the country continues to rely on imported petroleum products, an outrageous amount that can cripple the nation economically. Therefore, to save the nation from drifting completely to the precipice, the multi-billion-dollar refinery will boost Nigeria’s foreign exchange rate stability through the export of refined products.
Succinctly put, the coming on stream of the Dangote refinery is a game-changer that Nigeria so needs at this time. The refinery would not only change the economic narratives in Nigeria but the entire continent of Africa. Aliko Dangote has turned the tide towards a prosperous future for the continent. Indeed, this is a monopoly we most need and desire.
Odoma is a public affairs analyst based in Abuja.
Business
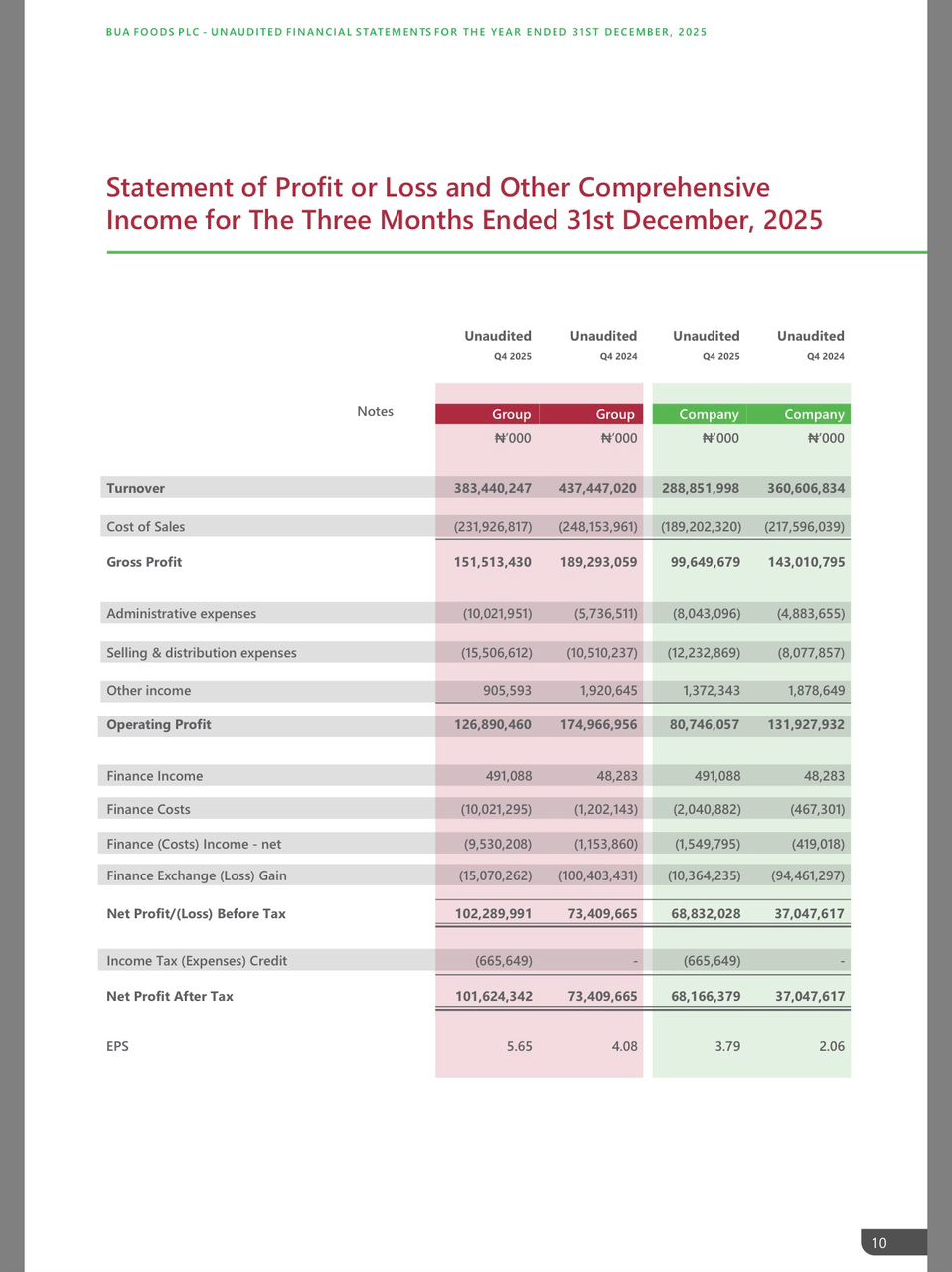
BUA Foods Records 91% Surge in Profit After Tax, Hits ₦508bn in 2025

BUA Foods Records 91% Surge in Profit After Tax, Hits ₦508bn in 2025
By femi Oyewale
Business
Adron Homes Unveils “Love for Love” Valentine Promo with Exciting Discounts, Luxury Gifts, and Travel Rewards

Adron Homes Unveils “Love for Love” Valentine Promo with Exciting Discounts, Luxury Gifts, and Travel Rewards
In celebration of the season of love, Adron Homes and Properties has announced the launch of its special Valentine campaign, “Love for Love” Promo, a customer-centric initiative designed to reward Nigerians who choose to express love through smart, lasting real estate investments.
The Love for Love Promo offers clients attractive discounts, flexible payment options, and an array of exclusive gift items, reinforcing Adron Homes’ commitment to making property ownership both rewarding and accessible. The campaign runs throughout the Valentine season and applies to the company’s wide portfolio of estates and housing projects strategically located across Nigeria.
Speaking on the promo, the company’s Managing Director, Mrs Adenike Ajobo, stated that the initiative is aimed at encouraging individuals and families to move beyond conventional Valentine gifts by investing in assets that secure their future. According to the company, love is best demonstrated through stability, legacy, and long-term value—principles that real estate ownership represents.
Under the promo structure, clients who make a payment of ₦100,000 receive cake, chocolates, and a bottle of wine, while those who pay ₦200,000 are rewarded with a Love Hamper. Payments of ₦500,000 attract a Love Hamper plus cake, and clients who pay ₦1,000,000 enjoy a choice of a Samsung phone or a Love Hamper with cake.
The rewards become increasingly premium as commitment grows. Clients who pay ₦5,000,000 receive either an iPad or an all-expenses-paid romantic getaway for a couple at one of Nigeria’s finest hotels, which includes two nights’ accommodation, special treats, and a Love Hamper. A payment of ₦10,000,000 comes with a choice of a Samsung Z Fold 7, three nights at a top-tier resort in Nigeria, or a full solar power installation.
For high-value investors, the Love for Love Promo delivers exceptional lifestyle experiences. Clients who pay ₦30,000,000 on land are rewarded with a three-night couple’s trip to Doha, Qatar, or South Africa, while purchasers of any Adron Homes house valued at ₦50,000,000 receive a double-door refrigerator.
The promo covers Adron Homes’ estates located in Lagos, Shimawa, Sagamu, Atan–Ota, Papalanto, Abeokuta, Ibadan, Osun, Ekiti, Abuja, Nasarawa, and Niger States, offering clients the opportunity to invest in fast-growing, strategically positioned communities nationwide.
Adron Homes reiterated that beyond the incentives, the campaign underscores the company’s strong reputation for secure land titles, affordable pricing, strategic locations, and a proven legacy in real estate development.
As Valentine’s Day approaches, Adron Homes encourages Nigerians at home and in the diaspora to take advantage of the Love for Love Promo to enjoy exceptional value, exclusive rewards, and the opportunity to build a future rooted in love, security, and prosperity.
Business
Why Nigeria’s Banks Still on Shaky Ground with Big Profits, Weak Capital

*Why Nigeria’s Banks Still on Shaky Ground with Big Profits, Weak Capital*
*BY BLAISE UDUNZE*
Despite the fragile 2024 economy grappling with inflation, currency volatility, and weak growth, Nigeria’s banking industry was widely portrayed as successful and strong amid triumphal headlines. The figures appeared to signal strength, resilience, and superior management as the Tier-1 banks such as Access Bank, Zenith Bank, GTBank, UBA, and First Bank of Nigeria, collectively reported profits approaching, and in some cases exceeding, N1 trillion. Surprisingly, a year later, these same banks touted as sound and solid are locked in a frenetic race to the capital markets, issuing rights offers and public placements back-to-back to meet the Central Bank of Nigeria’s N500 billion recapitalisation thresholds.
The contradiction is glaring. If Nigeria’s biggest banks are so profitable, why are they unable to internally fund their new capital requirements? Why have no fewer than 27 banks tapped the capital market in quick succession despite repeated assurances of balance-sheet robustness? And more fundamentally, what do these record profits actually say about the real health of the banking system?
The recapitalisation directive announced by the CBN in 2024 was ambitious by design. Banks with international licences were required to raise minimum capital to N500 billion by March 2026, while national and regional banks faced lower but still substantial thresholds ranging from N200 billion to N50 billion, respectively. Looking at the policy, it was sold as a modern reform meant to make banks stronger, more resilient in tough times, and better able to support major long-term economic development. In theory, strong banks should welcome such reforms. In practice, the scramble that followed has exposed uncomfortable truths about the structure of bank profitability in Nigeria.
At the heart of the inconsistency is a fundamental misunderstanding often encouraged by the banks themselves between profits and capital. Unknown to many, profitability, no matter how impressive, does not automatically translate into regulatory capital. Primarily, the CBN’s recapitalisation framework actually focuses on money paid in by shareholders when buying shares, fresh equity injected by investors over retained earnings or profits that exist mainly on paper.
This distinction matters because much of the profit surge recorded in 2024 and early 2025 was neither cash-generative nor sustainably repeatable. A significant portion of those headline banks’ profits reported actually came from foreign exchange revaluation gains following the sharp fall of the naira after exchange-rate unification. The industry witnessed that banks’ holding dollar-denominated assets their books showed bigger numbers as their balance sheets swell in naira terms, creating enormous paper profits without a corresponding improvement in underlying operational strength. These gains inflated income statements but did little to strengthen core capital, especially after the CBN barred banks from using FX revaluation gains for dividends or routine operations. In effect, banks looked richer without becoming stronger.
Beyond FX effects, Nigerian banks have increasingly relied on non-interest income fees, charges, and transaction levies to drive profitability. While this model is lucrative, it does not necessarily deepen financial intermediation or expand productive lending. High profits built on customer charges rather than loan growth offer limited support for long-term balance-sheet expansion. They also leave banks vulnerable when macroeconomic conditions shift, as is now happening.
Indeed, the recapitalisation exercise coincides with a turning point in the monetary cycle. The extraordinary conditions that supported bank earnings in 2024 and 2025 are beginning to unwind. Analysts now warn that Nigerian banks are approaching earnings reset, as net interest margins the backbone of traditional banking profitability, come under sustained pressure.
Renaissance Capital, in a January note, projects that major banks including Zenith, GTCO, Access Holdings, and UBA will struggle to deliver earnings growth in 2026 comparable to recent performance.
In a real sense, the CBN is expected to lower interest rates by 400 to 500 basis points because inflation is slowing down, and this means that banks will earn less on loans and government bonds, but they may not be able to quickly lower the interest they pay on deposits or other debts. The cash reserve requirements are still elevated, which does not earn interest; banks can’t easily increase or expand lending investments to make up for lower returns. The implications are significant. Net interest margin, the difference between what banks earn on loans and investments and what they pay on deposits, is poised to contract. Deposit competition is intensifying as lenders fight to shore up liquidity ahead of recapitalisation deadlines, pushing up funding costs. At the same time, yields on treasury bills and bonds, long a safe and lucrative haven for banks are expected to soften in a lower-rate environment. The result is a narrowing profit cushion just as banks are being asked to carry far larger equity bases.
Compounding this challenge is the fading of FX revaluation windfalls. With the naira relatively more stable in early 2026, the non-cash gains that once flattered bank earnings have largely evaporated. What remains is the less glamorous reality of core banking operations: credit risk management, cost efficiency, and genuine loan growth in a sluggish economy. In this new environment, maintaining headline profits will be far harder, even before accounting for the dilutive impact of recapitalisation.
That dilution is another underappreciated consequence of the capital rush. Massive share issuances mean that even if banks manage to sustain absolute profit levels, earnings per share and return on equity are likely to decline. Zenith, Access, UBA, and others are dramatically increasing their share counts. The same earnings pie is now being divided among many more shareholders, making individual returns leaner than during the pre-recapitalisation boom. For investors, the optics of strong profits may soon give way to the reality of weaker per-share performance.
Yet banks have pressed ahead, not only out of regulatory necessity but also strategic calculation.
During this period of recapitalization, investors are interested in the stock market with optimism, especially about bank shares, as banks are raising fresh capital, and this makes it easier to attract investments. This has become a season for the management teams to seize the moment to raise funds at relatively attractive valuations, strengthen ownership positions, and position themselves for post-recapitalisation dominance. In several cases, major shareholders and insiders have increased their stakes, as projected in the media, signalling confidence in long-term prospects even as near-term returns face pressure.
There is also a broader structural ambition at play. Well-capitalised banks can take on larger single obligor exposures, finance infrastructure projects, expand regionally, and compete more credibly with pan-African and global peers. From this perspective, recapitalisation is not merely about compliance but about reshaping the competitive hierarchy of Nigerian banking. What will be witnessed in the industry is that those who succeed will emerge larger, fewer, and more powerful. Those that fail will be forced into consolidation, retreat, or irrelevance.
For the wider economy, the outcome is ambiguous. Stronger banks with deeper capital buffers could improve systemic stability and enhance Nigeria’s ability to fund long-term development. The point is that while merging or consolidating banks may make them safer, it can also harm the market and the economy because it will reduce competition, let a few banks dominate, and encourage them to earn easy money from bonds and fees instead of funding real businesses. The truth be told, injecting more capital into the banks without complementary reforms in credit infrastructure, risk-sharing mechanisms, and fiscal discipline, isn’t enough as the aforementioned reforms are also needed.
The rush as exposed in this period, is that the moment Nigerian banks started raising new capital, the glaring reality behind their reported profits became clearer, that profits weren’t purely from good management, while the financial industry is not as sound and strong as its headline figures. The fact that trillion-naira profit banks must return repeatedly to shareholders for fresh capital is not a sign of excess strength, but of structural imbalance.
With the deadline for banks to raise new capital coming soon, by 31 March 2026, the focus has shifted from just raising N500 billion. N200 billion or N50 billion to think about the future shape and quality of Nigeria’s financial industry, or what it will actually look like afterward. Will recapitalisation mark a turning point toward deeper intermediation, lower dependence on speculative gains, and stronger support for economic growth? Or will it simply reset the numbers while leaving underlying incentives unchanged?
The answer will define the next chapter of Nigerian banking long after the capital market roadshows have ended and the profit headlines have faded.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: [email protected]
-

 celebrity radar - gossips6 months ago
celebrity radar - gossips6 months agoWhy Babangida’s Hilltop Home Became Nigeria’s Political “Mecca”
-

 society5 months ago
society5 months agoPower is a Loan, Not a Possession: The Sacred Duty of Planting People
-

 Business6 months ago
Business6 months agoBatsumi Travel CEO Lisa Sebogodi Wins Prestigious Africa Travel 100 Women Award
-

 news6 months ago
news6 months agoTHE APPOINTMENT OF WASIU AYINDE BY THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AS AN AMBASSADOR SOUNDS EMBARRASSING