Politics
Nigerians, Are You Better Than You Were Two Years Ago?
Nigerians, Are You Better Than You Were Two Years Ago?
By Gbenga Shaba
In 2025, a critical question resonates across Nigeria: “Am I better off today than I was yesterday?” For the vast majority of Nigerians, this is not a rhetorical exercise but a stark, lived reality, whispered in homes fractured by hunger and screamed in the silent desperation of stalled ambitions. From the bustling arteries of Lagos to the tranquil villages of Lafia, the answer, tragically, is a resounding no. Since the return to democratic governance in 1999, despite five presidents promising a brighter dawn, each new regime seems to bring less hope and more profound hardship.
The very essence of democracy, upon which its foundations were laid in 1999, promised something profoundly transformative: a demonstrably better life. This envisioned reality was not abstract; it meant the assurance of food on the table, consistent electricity, affordable healthcare, quality education, and jobs that could cover essential expenses and leave a little for life’s simple pleasures. Instead, Nigerians have largely received a relentless succession of economic experiments, a recurring drama surrounding fuel subsidies that consistently ends in public pain, a notoriously fragile national currency, and a poverty rate that has ballooned to alarming and unprecedented levels.
Empirical Comparisons Of Key Economic Indicators Across Administrations
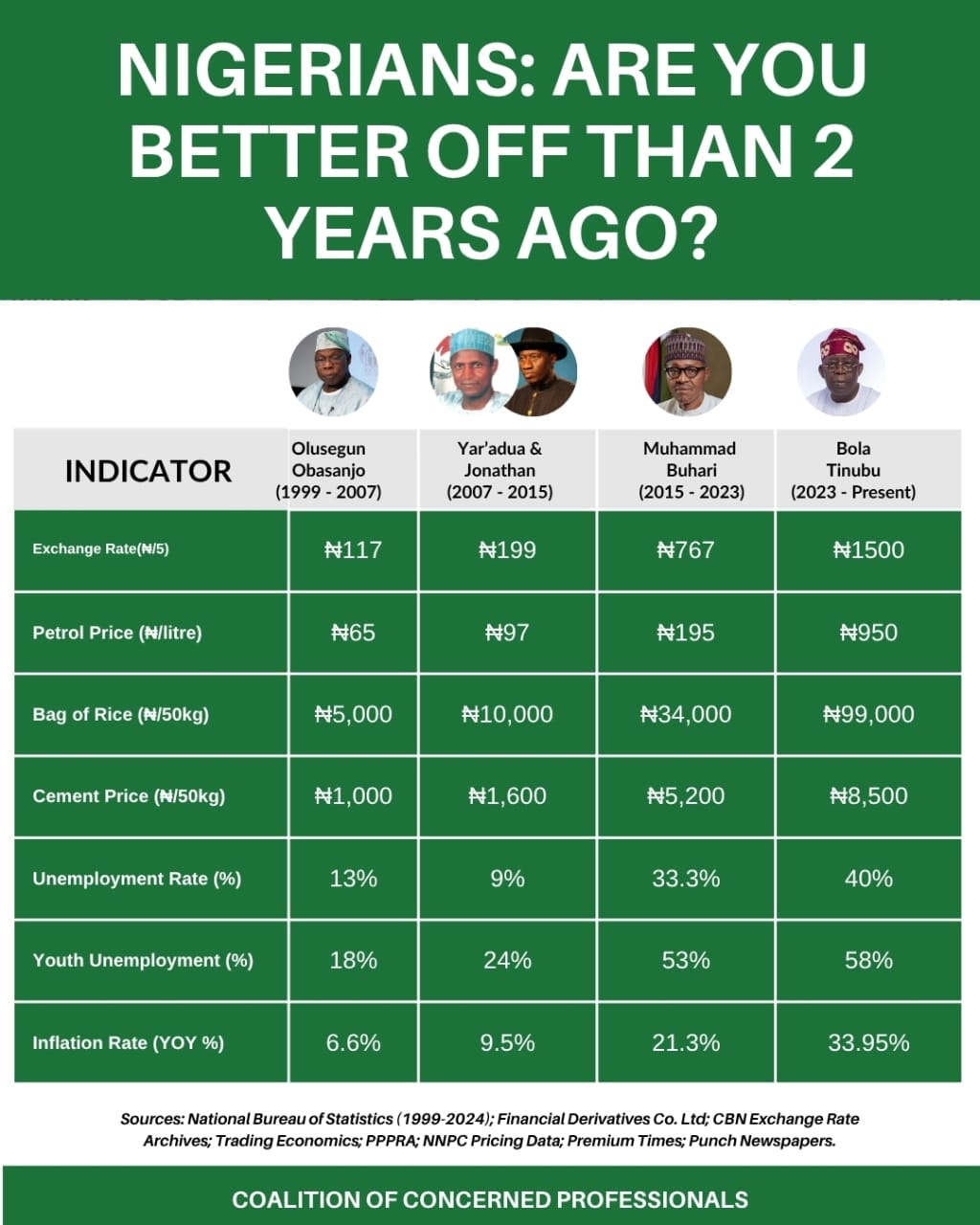
Empirical comparisons of key economic indicators across administrations reveal a consistently worsening pattern for the average citizen. A single litre of petrol now commands a price that, for many, exceeds a worker’s entire daily wage. In 1999, a litre of petrol cost approximately eleven naira. In 2025, that same litre costs well over seven hundred naira, a staggering sixty-threefold increase. The Nigerian naira, once trading at a relatively stable eighty to the United States dollar in 1999, now fluctuates precariously around one thousand four hundred and fifty to one thousand five hundred naira to the dollar, according to recent figures from financial markets. This represents an almost eighteenfold depreciation. As of July 2025, the naira trades around one thousand five hundred and twenty-eight naira to the dollar in the official window.
Inflation
Inflation, a voracious and unseen predator, devours incomes with the efficiency of termites in a wooden hut, leaving behind only the husks of diminished purchasing power. While hovering in single digits in 1999, the latest figures for May 2025 indicate headline inflation hovering around twenty-two point nine seven percent, with food inflation soaring to over forty percent. This means the cost of basic food items is increasing at an almost uncontrollable rate, eroding every gain. While the national minimum wage has nominally grown tenfold since 1999, now standing at thirty thousand naira, its real value has been devastatingly eroded by the relentless march of inflation. A nominal increase means little when purchasing power is decimated.
The Poverty Rate
The poverty rate, a stark measure of human well-being, has regrettably risen again. As of the latest multidimensional poverty index report, over one hundred and thirty-three million Nigerians, representing approximately sixty-three percent of the population, are now living in multidimensional poverty, lacking access to basic services and decent living standards.
This is not merely an economic crisis that can be neatly categorized within macroeconomic models. It is a profound national trauma etched onto the faces of its citizens. The cost of essential staples like rice and garri, the burden of transport fares, the escalating burden of rent, the prohibitive expense of school fees, and even the price of a sachet of water have multiplied severalfold in a short period. An average family in Kogi or Kano, which in 2005 could budget approximately five thousand naira for a week’s meals, now requires over thirty thousand naira to feed the same household. Chillingly, for this increased expenditure, the quality and nutritional value of the food consumed is often worse, a tragic testament to compromised living standards.
The current economic strain has become an oppressive weight, crushing aspirations and fostering widespread despair. Mrs Uzo, a mother in Aba, can no longer afford life-saving asthma medication for her young son. Tunde, a bright university graduate in Lagos, precariously sells phone accessories from a wheelbarrow, his dreams of a professional career indefinitely deferred. Amina, a widowed mother in Bauchi, makes the agonizing decision to skip meals herself so her children might at least have something to eat. These are the vivid and heart-wrenching realities and the raw, personal toll of abstract numbers and economic policies.
President Olusegun Obasanjo Vs Now
Under President Olusegun Obasanjo from 1999 to 2007, the administration embarked on broad and ambitious economic reforms. A landmark achievement was the successful negotiation of eighteen billion dollars in foreign debt relief through the Paris Club, significantly unburdening the national treasury. His tenure also oversaw the crucial consolidation of Nigeria’s banking sector. Perhaps most transformative was the advent of the telecom revolution, with GSM lines expanding explosively, birthing a dynamic new middle class. Macroeconomic stability was relatively sustained, inflation was managed, and real GDP demonstrated steady growth. The national minimum wage doubled, and poverty rates fell by a commendable eleven percentage points.
President Umaru Musa Yar’Adua and President Goodluck Jonathan Vs Now
During the administration of President Umaru Musa Yar’Adua and President Goodluck Jonathan from 2007 to 2010, despite electoral controversy and illness, a significant achievement was the Niger Delta Amnesty Programme, which restored stability and crucial oil output. While ambitious reforms were not fully realized, the renewed focus on the rule of law offered hope. Economically, inflation rose, reaching eleven point five eight percent in 2008 and twelve point five four percent in 2009, while poverty spiked by eight percent.
From 2010 to 2015, President Goodluck Jonathan and Vice President Namadi Sambo oversaw a period when Nigeria experienced a surge in GDP growth, propelled by high global oil prices. A rebasing exercise positioned Nigeria as Africa’s largest economy. However, this impressive GDP growth did not fully translate into real prosperity for the majority, and inequality widened. The power sector privatization largely failed to deliver stable electricity, and the Occupy Nigeria movement in 2012 highlighted growing discontent over fuel subsidy removal. Despite these challenges, poverty did decline marginally, and the agricultural sector saw reforms. Youth-targeted programs like YouWin provided some relief.
President Muhammadu Buhari and Vice President Yemi Osinbajo Also?
The administration of President Muhammadu Buhari and Vice President Yemi Osinbajo from 2015 to 2023 was heralded by many as a messianic anti-corruption movement, promising sweeping changes. It recorded successes in mainstreaming social investments and other programs. Significant investments were made in infrastructure projects, and social intervention programs were implemented to alleviate poverty and unemployment. However, the initial dream of revitalization soon withered under a cascade of economic shocks. A precipitous crash in global oil prices in 2016 triggered Nigeria’s first recession in decades. By 2020, the unforeseen onslaught of the COVID-19 pandemic dealt another devastating blow, knocking the economy into yet another tailspin and marking two recessions within a single tenure. Inflation soared to unprecedented heights, becoming a daily torment for households. Jobs disappeared at an alarming rate, exacerbating an already dire unemployment crisis. The naira was devalued not once but twice over, further eroding purchasing power and making imports prohibitively expensive. The undeniable reality for the average Nigerian was one of increasing poverty, pervasive hunger, and a deepening sense of hopelessness. While the minimum wage was eventually raised to thirty thousand naira, it was swiftly outpaced by the relentless surge in food inflation and punitive fuel price hikes, rendering the increment almost immediately insufficient.
The last 2 years!
President Bola Ahmed Tinubu and Vice President Kashim Shettima came into office in 2023 on the campaign theme of Renewed Hope. However, their administration’s immediate and simultaneous removal of the fuel subsidy and floating of the naira sent seismic shockwaves through the fragile economy. Within days, transport costs tripled, and the price of a common loaf of bread skyrocketed. Many families were forced to pull their children out of school. Markets emptied, and small businesses closed in droves. The economy, already bruised, began to fracture under the pressure.
The government maintains that these drastic measures are necessary pains that will eventually lead to broader prosperity. This argument is not new, but Nigerians are profoundly tired of deferred dreams and promises of future abundance that never materialize. The pressing question remains: how long must the poor wait for the promised benefits, and how much more suffering can be endured?
True reform, the kind that genuinely uplifts a nation, fundamentally puts its people first. It is not about abstract macroeconomic numbers or accolades from multilateral financial institutions. It is, first and foremost, about the tangible impact on the lives of ordinary citizens. A truly people-oriented leadership would embody a different approach. It would push for social equity, prioritize local content development, and champion grassroots empowerment. Where the current approach removes subsidies without adequate cushioning, a people-oriented leadership would meticulously sequence reforms, implementing robust safety nets and palliative measures. Where the naira has been fully floated, a people-oriented leadership would carefully protect strategic sectors and essential commodities from volatile market forces. And crucially, where blame is cast upon the past, a people-oriented leadership would believe in co-creating the future with the people through inclusive dialogue and participatory governance.
Economic Indicators
A Declining Trajectory
Empirical comparisons of key economic indicators across administrations reveal a consistently worsening pattern for the average citizen.
Petrol Price: A single litre of petrol now commands a price that, for many, exceeds a worker’s entire daily wage. In 1999, a litre of petrol cost approximately eleven Naira. In 2025, that same litre costs well over seven hundred Naira, a staggering sixty-three-fold increase.
Exchange Rate: The Nigerian Naira, once trading at a relatively stable eighty to the United States Dollar in 1999, now fluctuates precariously around one thousand four hundred and fifty to one thousand five hundred Naira to the dollar, according to recent figures from financial markets. This represents an almost eighteen-fold depreciation. As of July 2025, the Naira trades around one thousand five hundred and twenty-eight Naira to the dollar in the official window.
Inflation: Inflation, a voracious, unseen predator, devours incomes with the efficiency of termites in a wooden hut, leaving behind only the husks of diminished purchasing power. While hovering in single digits in 1999, the latest figures for May 2025 indicate headline inflation hovering around twenty-two point nine-seven percent, with food inflation soaring to over forty percent. This means the cost of basic food items is increasing at an almost uncontrollable rate, eroding every gain.
Minimum Wage: While the national minimum wage has nominally grown tenfold since 1999, now standing at thirty thousand Naira, its real value has been devastatingly eroded by the relentless march of inflation. A nominal increase means little when purchasing power is decimated.
Poverty Rate: The poverty rate, a stark measure of human well-being, has regrettably risen again. As of the latest multidimensional poverty index report, over one hundred and thirty-three million Nigerians, representing approximately sixty-three percent of the population, are now living in multidimensional poverty, lacking access to basic services and living standards.
The difference is crystal clear. One governs with an eye on the boardroom. The other governs for the marketplace, for the common man and woman, for the struggling family. As 2025 unfolds, the fundamental question persists, demanding an answer. Ask the mechanic in Minna, the teacher in Ikare, or the tomato seller in Mile Twelve. Their answer, spoken in the language of hunger and hardship, is tragically and unambiguously the same: no, we are not better off.
Until Nigeria consistently and genuinely puts its people first, it will remain trapped in a disheartening cycle of unfulfilled promises. Genuine change is not merely about new faces in power. It is about an unwavering focus on serving the people those numbers are meant to represent and uplift. The true measure of a nation’s progress lies not in its statistical achievements but in the tangible improvement of the lives of its most vulnerable citizens. Only then can the answer to that profound question finally be a resounding and joyous yes.
Gbenga Shaba is a journalist and an analyst from Lagos State, Nigeria.
Politics
Kogi’s Quiet Shift: Reviewing Governor Ododo’s First 24 Months in Office

Kogi’s Quiet Shift: Reviewing Governor Ododo’s First 24 Months in Office
By Rowland Olonishuwa
On Tuesday, Kogi State paused to mark two years since Alhaji Ahmed Usman Ododo took the oath as Executive Governor. Across government circles, community halls, and everyday conversations, the anniversary was more than a date on the calendar; it was a milestone that invites both reflection and renewed optimism. A moment to look back at how far the state has travelled in just twenty-four months, and where it is heading next.
Since assuming office in January 2024, Ododo has steered the state through a period of measured consolidation, delivering strategic interventions across security, infrastructure, human capital, and economic revitalisation that are beginning to translate into real improvements for residents.
Governor Ododo stepped into office at a time when expectations were high, and confidence in public institutions needed rebuilding.
His response to these was not loud declarations, but steady consolidation, strengthening structures, restoring order in governance, and setting a clear direction. Over time, that calm approach has become his signature: leadership that listens first, plans carefully, and moves with purpose.
Security has remained the most urgent concern for Nigerians, and Kogi residents are no exceptions; the Ododo-led administration has treated it as such. From deploying surveillance drones to support intelligence operations to recruiting and integrating local hunters and vigilante personnel into formal security frameworks, the government has built a layered safety net.
For farmers returning to their fields, travellers moving along highways, and families in rural communities, the impact is simple and deeply personal: fewer fears, quicker response, and growing confidence that the government is present and concerned about the ordinary people.
Infrastructural development has followed the same practical logic. Roads have been rehabilitated, easing movement for traders and commuters. Budget priorities have shifted toward capital projects and human development, while revived facilities like the Confluence Rice Mill now provide farmers with real economic opportunity. For many households, this means better income prospects, stronger local trade, and renewed belief that development is no longer a distant promise.
Health and education are not left out; the Ododo-led administration has expanded free healthcare services and supported students through examination funding and institutional improvements.
Parents who once struggled with medical bills and school fees have felt relief. Young people preparing for their futures now see government investment not as abstract policy but as something that touches their daily lives.
Governance reforms, from civil service strengthening to new legislative frameworks, have quietly improved how government functions. Salaries are more predictable, public offices are more responsive, and local government structures are more coordinated. These may not always make headlines, but they shape how citizens experience leadership every day.
As the second year anniversary celebrations fade into routine today and Governor Ododo enters his third year in office, the true meaning of the anniversary will continue to linger on.
Two years may not have solved every challenge in the Confluence State -no government ever does, by the way- but they have set a tone of stability, responsiveness, and direction. The next phase will demand deeper impact, broader reach, and sustained security gains.
But for many in Kogi State, the story of the past twenty-four months is already clear: steady hands on the wheel, and a journey that is firmly underway.
Olonishuwa is the Editor-in-Chief of Newshubmag.com. He writes from Ilorin
Politics
Lagos Assembly Debunks Abuja House Rumour, Warns Against Election Season Propaganda

Lagos Assembly Debunks Abuja House Rumour, Warns Against Election Season Propaganda
The Lagos State House of Assembly has described as misleading and mischievous the widespread misinformation that it budgeted for the purchase of houses in Abuja for its members in the 2026 Appropriation Law.
This rebuttal is contained in a statement jointly signed by Hon. Stephen Ogundipe, Chairman, House Committee on Information, Strategy, and Security, and Hon. Sa’ad Olumoh, Chairman, House Committee on Economic Planning and Budget.
Describing the report as a deliberate and disturbing falsehood being peddled by patently ignorant people, the statement reads, “There is no provision whatsoever in the 2026 Budget for the purchase of houses in Abuja or anywhere else for members of the Lagos State House of Assembly. The report is a complete fabrication and a product of political mischief intended to misinform the public.
“The Lagos State House of Assembly does not operate in Abuja. Our constitutional responsibilities, constituencies, and legislative duties are entirely within Lagos State. It is, therefore, illogical, irrational, and irresponsible for anyone to suggest that legislators would appropriate public funds for personal housing outside their jurisdiction.”
The statement emphasised that the budget is already in the public domain and accessible for scrutiny by discerning Lagosians and Nigerians alike. It reiterated that the Lagos State Government operates a transparent budget that speaks to the needs of the people and the demands of a megalopolis.
“We view this rumour as part of a wider attempt at election-season propaganda, designed to erode public trust, sow discord, and malign democratic institutions.”
The chairmen further clarified that the 2026 capital expenditure of the House of Assembly is less than 0.04% of the total CAPEX of the state, which clearly demonstrates the culture of prudence, accountability, and fiscal responsibility that guides the legislature. However, they noted, “Historically, the House does not even access up to its approved budget in many fiscal years.”
They stressed that the Assembly remains fully committed to excellence, transparency, good governance, and the collective welfare of the people of Lagos State, in line with the objectives of the 2026 Budget of Shared Prosperity.
“We therefore challenge those behind this harebrained allegation to produce credible evidence or retract their statements forthwith. Failure to do so may attract appropriate legal actions.
“We urge Lagosians and the general public to disregard this baseless rumour and always verify information from official and credible sources.”
Politics
Democracy in the Crosshairs: How Nigeria’s Ruling APC Weaponises Power and Silences Dissent

Democracy in the Crosshairs: How Nigeria’s Ruling APC Weaponises Power and Silences Dissent.
By George Omagbemi Sylvester | Published by saharaweeklyng.com
“Tinubu’s Government, the EFCC and the Strategic Undermining of Opposition Governors”.
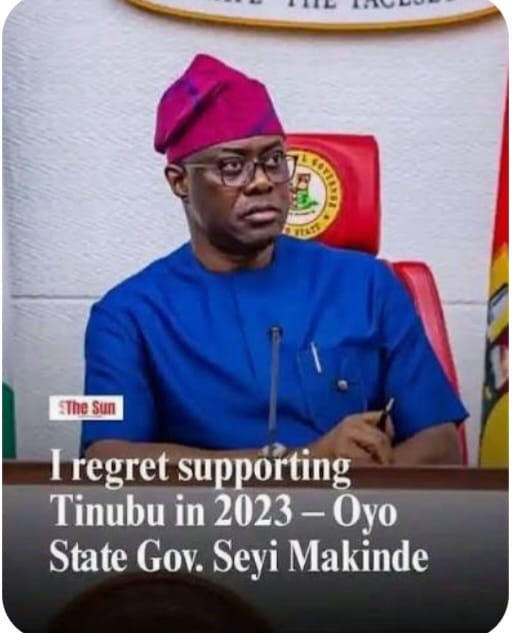
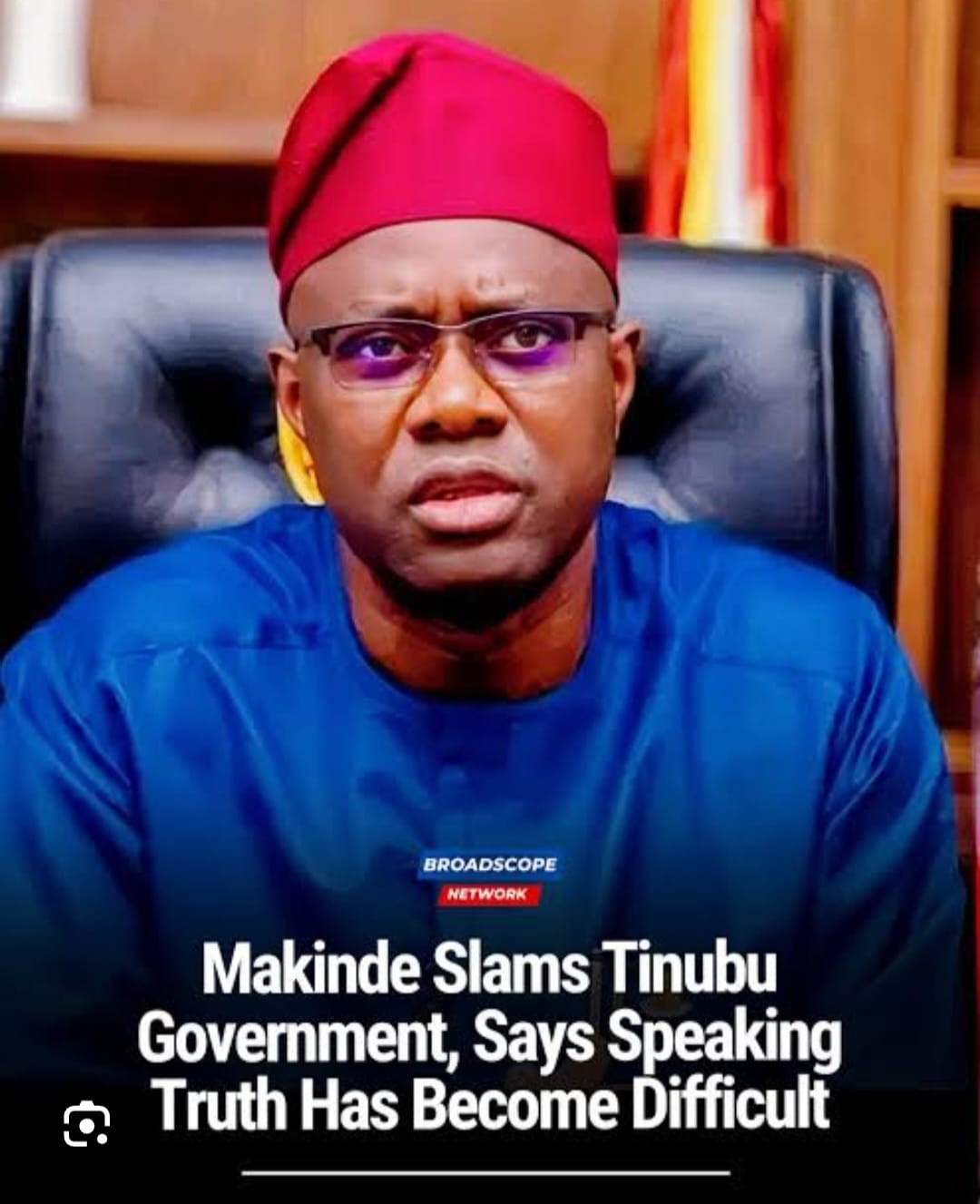
In a striking indictment of Nigeria’s current political reality, Governor Seyi Makinde of Oyo State declared that “you cannot speak truth to power in this dispensation”, directly accusing the administration of President Bola Ahmed Tinubu of intolerance for dissent and an erosion of democratic norms.
Makinde’s remarks (made during a public event in Ibadan on January 25, 2026) were more than a local governor’s lament. They crystallised a mounting national frustration: that Nigeria’s political landscape has tilted dangerously toward executive overreach, institutional capture and political engineering.
This narrative is not isolated. Across Nigeria, governors from opposition parties have defected to the ruling All Progressives Congress (APC) in numbers unprecedented in the nation’s democratic history. Critics argue that these defections are not merely voluntary political choices, but part of a strategic pressure campaign leveraging federal power and institutions to fracture opposition influence.
At its centre lies Nigeria’s principal anti-graft agency – the Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC).
The EFCC: Anti-Graft Agency or Political Instrument? Founded to combat corruption, the EFCC’s constitutional mandate is to investigate and prosecute financial and economic crimes across public and private sectors. Its legal independence is enshrined in statute and it has historically pursued high-profile cases, including recovery of nearly $500 million in illicit assets in a single year, demonstrating its capacity for tackling corruption.
However, critics now claim that under the Tinubu administration, the EFCC’s prosecutorial power is being perceived (if not deployed) as a political instrument.
Opposition leaders, including former Vice President Atiku Abubakar and coalition parties such as the African Democratic Congress (ADC), have publicly accused the federal government of using anti-corruption agencies to intimidate opposition figures and governors, effectively pressuring them into aligning with the APC.
In a statement released in December 2025, opposition figures alleged that institutions such as the EFCC, the Nigerian Police and the Independent Corrupt Practices and Other Related Offences Commission were being selectively wielded to weaken political competitors rather than combat financial crime impartially.
This is not merely rhetorical noise. The opposition’s grievances centre on several observable patterns:
Reopened or New Investigations Against Opposition Figures: The ADC pointed to recent abnormal reactivation of long-dormant cases or new inquiries into financial activities involving senior opposition politicians. These, they argue, often arise shortly before critical elections or political realignments.
Alleged Differential Treatment: According to opponents of the current administration, individuals who have defected to the APC appear less likely to face sustained legal scrutiny or prosecution in EFCC proceedings, even in cases of credible allegations of mismanagement.
Timing of Actions: The timing of certain high-profile investigations, emerging ahead of the 2027 general elections, reinforces perceptions that anti-graft measures are tailored to political cycles rather than legal merit.
The EFCC and Presidency have publicly denied these allegations, insisting that the commission operates independently and pursues corruption irrespective of political affiliation and that Nigeria’s democratic freedoms (including party choice and mobility) remain intact.
Yet the perception of bias, once systemic, is hard to erase, especially when political actors deploy powerful state machinery with strategic timing and selective intensity.
Defections and Power Realignment: A Democracy at Risk? Since 2023 and particularly through 2025, a remarkable number of state governors and senior political leaders have crossed over from opposition parties (notably the Peoples Democratic Party – PDP) to the APC. Though defections are normal in Nigeria’s fluid political system, the scale and speed in recent years are historically noteworthy, raising critical questions about underlying incentives.
The SaharaWeeklyNG reported Makinde’s comments within the broader context of a political climate where dissenting voices face greater obstacles than at any time in recent democratic memory.
Governors who remain in opposition find themselves squeezed between growing federal assertiveness and dwindling political capital. Some analysts argue that the combination of federal resource control, political appointments and influence over public agencies exerts tangible pressure on subnational leaders to align with the ruling party for political survival. This dynamic, they contend, undermines competitive party politics and weakens Nigeria’s multiparty democracy.
Speaking Truth to Power: What Makinde’s Critique Exposes. Governor Makinde’s core grievance (that it is increasingly difficult, perhaps perilous, to speak truth to power) resonates widely among civil society actors, political analysts and democratic advocates:
“YOU CANNOT SPEAK TRUTH TO POWER IN THIS DISPENSATION,” Makinde declared, specifically citing the government’s handling of contentious tax reform bills as an example where dissent was neither welcomed nor transparently debated.
Makinde’s critique reflects deeper structural concerns:
Exclusion of Key Stakeholders: Opposition leaders and state executives report being marginalised from meaningful consultation on national policies affecting federal-state relations, revenue sharing and fiscal reforms.
Institutional Intimidation: The perception that state politicians become targets of federal legal scrutiny after taking firm oppositional stances (real or perceived) discourages robust democratic debate.
Erosion of Opposition Space: A symbiotic effect of party defections and institutional pressure is a shrinking viable space for genuine political opposition, weakening checks and balances essential to democratic governance.
A respected political scientist, Dr. Aisha Bello of the University of Lagos, recently argued that “when opposition becomes fraught with state leverage instead of ideological competition, the very foundation of democratic contestation collapses,” adding that “a government that shies away from criticism risks inversion into autocracy.”
Another expert, Prof. Chinedu Eze, former dean of political studies at Ahmadu Bello University, warned that “selective use of anti-corruption agencies as political tools corrodes public trust and ultimately delegates justice into the hands of incumbents rather than independent courts.” These observations echo growing public skepticism.
The Way Forward: Strengthening Democracy and Institutions. Nigeria’s path forward depends on restoring confidence in democratic norms and institutional independence.
Transparent EFCC Processes: Civil society groups and legal scholars are advocating for enhanced transparency in anti-graft investigations, including clear prosecutorial thresholds and independent audits of case initiation and closures.
Judicial Oversight: Strengthening the judiciary’s capacity and independence is critical to ensuring that allegations of political weaponisation do not go unchecked. Courts must remain the ultimate arbiters of evidence and guilt.
Political Reforms: Advocates demand reforms to party financing, federal-state fiscal relations, and consultation mechanisms to reduce incentives for defections driven by federal resource leverage.
Public Engagement: A more informed and engaged civil society, anchored by independent media and civic education, must hold both government and opposition accountable for adherence to democratic principles.
Beyond The Present Moment.
Governor Makinde’s assertion that it is no longer tenable to “speak truth to power” under the current administration reflects unsettling trends in Nigeria’s evolving democratic landscape. While the EFCC and the Presidency maintain that anti-corruption efforts are independent and constitutionally grounded, opposition leaders (backed by political data and patterns of defections) argue that state power is being used to consolidate one-party dominance and undermine political pluralism.
At this critical juncture, Nigeria must choose between entrenching competitive democracy or sliding toward a political monopoly where dissent is subdued, institutions compromised, and power concentrated.
For Nigeria’s democratic ideals to survive (and thrive) its leaders and citizens must ensure that speaking truth to power remains not a perilous act of defiance but an honoured pillar of national life.
-

 celebrity radar - gossips6 months ago
celebrity radar - gossips6 months agoWhy Babangida’s Hilltop Home Became Nigeria’s Political “Mecca”
-

 society6 months ago
society6 months agoPower is a Loan, Not a Possession: The Sacred Duty of Planting People
-

 Business6 months ago
Business6 months agoBatsumi Travel CEO Lisa Sebogodi Wins Prestigious Africa Travel 100 Women Award
-

 news6 months ago
news6 months agoTHE APPOINTMENT OF WASIU AYINDE BY THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AS AN AMBASSADOR SOUNDS EMBARRASSING