Business
TIN or Nothing: How Nigeria’s 2026 Tax Revolution Will Reshape Every Citizen’s Financial Future

TIN or Nothing: How Nigeria’s 2026 Tax Revolution Will Reshape Every Citizen’s Financial Future.
By George Omagbemi Sylvester | Published by Saharaweeklyng.com
No TIN, No Bank, No Business – Millions Risk Being Locked Out of the Economy Overnight.
In a country where CITIZENS ARE USED to BEING CAUGHT OFF GUARD by SUDDEN GOVERNMENT POLICIES, a silent storm is brewing that could paralyze millions of Nigerians by January 2026. The storm has three letters: TIN – Tax Identification Number.
For decades, Nigeria’s tax culture has been riddled with negligence, corruption and loopholes. Only a small fraction of the population pays tax, while government after government complains about low revenue generation and excessive reliance on oil. Today, however, the Federal Government has drawn a bold line in the sand: no TIN, no FINANCIAL ACCESS.
This is not a distant threat. It is a looming reality. By 2026, without a TIN, you may wake up to discover that your bank account has been blocked, your transactions halted and your business paralyzed. The government is shifting from rhetoric to enforcement and Nigerians must either prepare or face financial suffocation.
Why TIN Has Become the “MASTER KEY”.
Let us be blunt: Nigeria has one of the lowest tax-to-GDP ratios in the world, hovering at about 10% according to the World Bank (2023), compared to South Africa at 26%, Kenya at 18% and the OECD average of 34%. Less than 10% of Nigerians actually pay tax. For a country of over 200 million people, this is an economic tragedy.
Professor Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala, now Director-General of the World Trade Organization, once remarked:
“No nation can survive when its citizens refuse to contribute fairly to its revenue base. Oil cannot carry Nigeria forever.”
The government knows this. With declining oil revenue, mounting debt (over $114 billion as of 2024) and a growing population, Nigeria has no choice but to expand its tax net. The TIN is the weapon of choice.
By linking every financial service (banking, business registration, property transactions and even remittances) to a TIN, the government will effectively monitor economic activity and enforce compliance.
In plain terms: the TIN will become your new identity, more powerful than BVN or NIN.
The Silent Bank Blockade.
Unlike other government reforms that come with public campaigns, the TIN enforcement will arrive quietly. Don’t expect a press conference or ceremonial announcement. Instead, one morning in January 2026, you may log into your banking app and see a cold message:
“Service Unavailable – Provide TIN.”
That is how millions of Nigerians will be stranded. No withdrawal. No transfer. No school fees payment. No hospital bill settlement. Just silence.
Dr. Andrew Nevin, Chief Economist at PwC Nigeria, recently warned:
“The integration of tax identification into the financial system is inevitable. Those who fail to comply will simply be locked out of the economy. It is not punishment; it is structural reform.”
This is not scaremongering. This is fact.
Breaking the Myth: TIN Is Not Just for Companies.
A dangerous misconception is spreading: that TIN is only for companies or registered businesses. That is a big lie. The new law mandates every individual who operates a bank account (students, traders, freelancers, salary earners and retirees) to obtain a TIN.
Think of it as the government saying: “If you touch money in Nigeria, we must see you.”
For business owners, it goes further. A registered business will need both an individual TIN and a business TIN (linked to its CAC registration). No TIN, no contracts, no tenders, no access to loans.
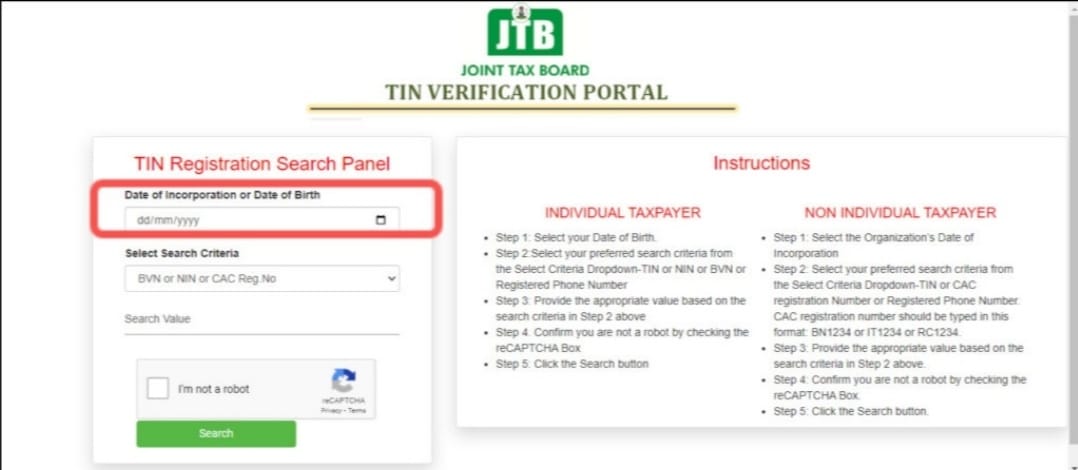
How to Get Your TIN Before the Deadline.
Thankfully, getting a TIN is not rocket science. It is free, simple and available both online and offline. Here is the practical breakdown:
For Individuals (Personal TIN):
Visit the Joint Tax Board (JTB) TIN registration portal online.
Or, walk into any Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS) office (soon to be renamed the National Revenue Service, NRS).
Carry the following:
NIN slip or National ID card
Utility bill (for address verification)
One passport photograph
Fill out a short form and request for your TIN.
Processing can take from the same day to a few days.
Take your TIN printout to your bank and update your records.
For Businesses (Business TIN):
Carry your Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC) certificate to FIRS.
Request for a business TIN (different from your personal one).
That’s it. Simple, but life-changing.
Why This Reform Is Inevitable.
Critics will argue that the government is punishing citizens who already suffer under poverty, inflation and unemployment. They are not wrong. As of 2025, inflation stands at 28.5%, unemployment at 33%, and over 133 million Nigerians live in multidimensional poverty (National Bureau of Statistics).
However, the counter-argument is sobering: Nigeria cannot continue as a non-tax-paying society. Without broad tax compliance, the country will remain dependent on loans, aid and oil; a recipe for disaster.
As the late Kofi Annan, former UN Secretary-General, once said:
“Tax is the price we pay for civilization. To evade tax is to steal from the poor.”
The Risks of Non-compliance.
Make no mistake: this is not a policy you can dodge. Every bank account, every transfer, every mobile wallet, every financial footprint will soon be tracked and linked to TIN.
Failure to comply means:
Blocked bank accounts
No access to loans or grants
Inability to register or run a business
Being excluded from government programs
Even potential legal consequences for tax evasion
In short: financial invisibility.
Lessons from Other Countries.
Nigeria is not the first to implement such a drastic tax reform.
South Africa links every financial transaction to a Tax Reference Number. Without it, you cannot open a bank account.
Kenya requires a Personal Identification Number (PIN) for property purchases, motor vehicle registration and financial dealings.
Ghana introduced the Ghana Card, which doubles as a tax ID and is mandatory for bank transactions.
Nigeria is only following the global trend. But unlike others, Nigeria’s rollout is more abrupt, more uncompromising and more far-reaching.
Preparing for the Inevitable.
Instead of complaining about government “WAHALA,” Nigerians must wake up to reality. 2026 will not wait for excuses. The choice is stark: either embrace the TIN revolution or become financially stranded.
Theologian John Wesley once said:
“Earn all you can, save all you can, give all you can; but also pay all you owe.”
Taxes are part of what we owe to the state.
Final Word.
If you are reading this, take a deep breath and understand: 2026 is not just another year. It is the year Nigeria will separate those who prepared from those who are stranded.
Do not be caught in the cold silence of a blocked bank app. Do not let ignorance or procrastination rob you of financial freedom.
Register for your TIN now. Not tomorrow. Not next month. Now.
In 2026, the three most powerful letters in Nigeria will not be APC, PDP or NIN.
They will be TIN.
Bank
Alpha Morgan to Host 19th Economic Review Webinar

Alpha Morgan to Host 19th Economic Review Webinar
In an economy shaped by constant shifts, the edge often belongs to those with the right information.
On Wednesday, February 25, 2026, Alpha Morgan Bank will host the 19th edition of its Economic Review Webinar, a high-level thought leadership session designed to equip businesses, investors, and individuals with timely financial and economic insight.
The session, which will hold live on Zoom at 10:00am WAT and will feature economist Bismarck Rewane, who will examine the key signals influencing Nigeria’s economic direction in 2026, including policy trends, market movements, and global developments shaping the local landscape.
With a consistent track record of delivering clarity in uncertain times, the Alpha Morgan Economic Review continues to provide practical context for decision-making in a dynamic environment.
Registration for the 19th Alpha Morgan Economic Review is free and can be completed via https://bit.ly/registeramerseries19
It is a bi-monthly platform that is open to the public and is held virtually.
Visit www.alphamorganbank to know more.
Business
GTBank Launches Quick Airtime Loan at 2.95%

GTBank Launches Quick Airtime Loan at 2.95%
Guaranty Trust Bank Ltd (GTBank), the flagship banking franchise of GTCO Plc, Africa’s leading financial services group, today announced the launch of Quick Airtime Loan, an innovative digital solution that gives customers instant access to airtime when they run out of call credit and have limited funds in their bank accounts, ensuring customers can stay connected when it matters most.
In today’s always-on world, running out of airtime is more than a minor inconvenience. It can mean missed opportunities, disrupted plans, and lost connections, often at the very moment when funds are tight, and options are limited. Quick Airtime Loan was created to solve this problem, offering customers instant access to airtime on credit, directly from their bank. With Quick Airtime Loan, eligible GTBank customers can access from ₦100 and up to ₦10,000 by dialing *737*90#. Available across all major mobile networks in Nigeria, the service will soon expand to include data loans, further strengthening its proposition as a reliable on-demand platform.
For years, the airtime credit market has been dominated by Telcos, where charges for this service are at 15%. GTBank is now changing the narrative by offering a customer-centric, bank-led digital alternative priced at 2.95%. Built on transparency, convenience and affordability, Quick Airtime Loan has the potential to broaden access to airtime, deliver meaningful cost savings for millions of Nigerians, and redefine how financial services show up in everyday life, not just in banking moments.
Commenting on the product launch, Miriam Olusanya, Managing Director of Guaranty Trust Bank Ltd, said: “Quick Airtime Loan reflects GTBank’s continued focus on delivering digital solutions that are relevant, accessible, and built around real customer needs. The solution underscores the power of a connected financial ecosystem, combining GTBank’s digital reach and lending expertise with the capabilities of HabariPay to deliver a smooth, end-to-end experience. By leveraging unique strengths across the Group, we are able to accelerate innovation, strengthen execution, and deliver a more integrated customer experience across all our service channels.”
Importantly, Quick Airtime Loan highlights GTCO’s evolution as a fully diversified financial services group. Leveraging HabariPay’s Squad, the solution reinforces the Group’s ecosystem proposition by bringing together banking, payment technology, and digital channels to deliver intuitive, one-stop experiences for customers.
With this new product launch, Guaranty Trust Bank is extending its legacy of pioneering digital-first solutions that have redefined customer access to financial services across the industry, building on the proven strength of its widely adopted QuickCredit offering and the convenience of the Bank’s iconic *737# USSD Banking platform.
About Guaranty Trust Bank
Guaranty Trust Bank (GTBank) is the flagship banking franchise of GTCO Plc, a leading financial services group with a strong presence across Africa and the United Kingdom. The Bank is widely recognized for its leadership in digital banking, customer experience, and innovative financial solutions that deliver value to individuals, businesses, and communities.
About HabariPay
HabariPay is the payments fintech subsidiary of GTCO Plc, focused on enabling fast, secure, and accessible digital payments for individuals and businesses. By integrating payments and digital technology, HabariPay supports innovative services that make everyday financial interactions simpler and more seamless.
Enquiries:
GTCO
Group Corporate Communication
[email protected]
+234-1-2715227
www.gtcoplc.com
Business
BUA Group, AD Ports Group and MAIR Group Launch Strategic Plan for World-Class Sugar and Agro-Logistics Hub at Khalifa Port

BUA Group, AD Ports Group and MAIR Group Sign MoU to Explore Collaboration in Sugar Refining, Agro-Industrial Development, and Integrated Global Logistics Solutions
Abu Dhabi, UAE – Monday, 16th February 2026
BUA Group, AD Ports Group, and MAIR Group of Abu Dhabi today signed a strategic Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to explore collaboration in sugar refining, agro-industrial development, and integrated global logistics solutions. The partnership aims to create a world-class platform that strengthens regional food security, supports industrial diversification, and reinforces Abu Dhabi’s position as a hub for trade and manufacturing.
The proposed collaboration will leverage BUA Group’s industrial and logistics expertise, Khalifa Port’s world-class infrastructure, and AD Ports Group’s operational experience. The initiative aligns with the objectives of the UAE Food Security Strategy 2051, which seeks to position the UAE as a global leader in sustainable food production and resilient supply chains. It also aligns with Nigeria’s food production- and export-oriented agricultural transformation agenda, focused on scaling domestic capacity, strengthening value addition, improving post-harvest logistics, and unlocking new markets for Nigerian produce across the Middle East, Asia, and beyond.

Photo Caption: L-R: Kabiru Rabiu, Group Executive Director, BUA Group; Cpt. Mohammed J. Al Shamisi, MD/Group CEO, AD Ports Group; Saif Al Mazrouei, CEO (Ports Cluster) AD Ports Group; Abdul Samad Rabiu, Founder/Executive Chairman, BUA Group; and Steve Green, Group CFO, MAIR Group
Through structured aggregation, processing, storage, and maritime export channels, the partnership is designed to reduce supply chain inefficiencies, enhance traceability and quality standards, and also create a predictable trade corridor between West Africa and the Gulf.
BUA Group—recognised as one of Africa’s largest and most diversified conglomerates, with major investments across sugar refining, food production, flour milling, cement manufacturing, and infrastructure- brings extensive industrial expertise and large-scale operational capability to the venture. MAIR Group will provide strategic support in developing integrated logistics and agro-industrial solutions, creating a seamless platform for production, storage, and distribution.
Abdul Samad Rabiu, Founder and Chairman of BUA Group, said:
“This MoU marks an important milestone in BUA’s international expansion and reflects our long-term vision of building globally competitive industrial platforms. Together with AD Ports Group and MAIR Group, we aim to develop sustainable food production and logistics solutions that strengthen regional supply chains and support the UAE’s Food Security Strategy 2051.”
He further added that, “This partnership represents not just a commercial arrangement but a strategic food corridor anchored on shared economic ambition, resilient infrastructure, and disciplined execution, reinforcing long-term food security objectives for both nations.”
A representative of MAIR Group added:
“This collaboration underscores our commitment to advancing strategic industries in Abu Dhabi and building integrated solutions that reinforce the UAE’s position as a global hub for trade, food security, and industrial excellence.”
A spokesperson from AD Ports Group commented:
“Our partnership with BUA Group and MAIR Group highlights Khalifa Port’s role as a catalyst for high-impact industrial investments. This initiative will enhance regional food security, strengthen global trade connectivity, and support Abu Dhabi’s economic diversification goals.”
This MoU marks a historic collaboration that combines world-class infrastructure, industrial expertise, and strategic vision, setting the stage for a sustainable and resilient food and logistics ecosystem that will benefit the UAE, the region, and global markets alike.
-

 celebrity radar - gossips6 months ago
celebrity radar - gossips6 months agoWhy Babangida’s Hilltop Home Became Nigeria’s Political “Mecca”
-

 society6 months ago
society6 months agoPower is a Loan, Not a Possession: The Sacred Duty of Planting People
-

 news6 months ago
news6 months agoTHE APPOINTMENT OF WASIU AYINDE BY THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AS AN AMBASSADOR SOUNDS EMBARRASSING
-

 society5 months ago
society5 months agoReligion: Africa’s Oldest Weapon of Enslavement and the Forgotten Truth