Business
Nigeria’s Poverty Crisis: A World Bank Perspective on the Deepening Divide

Nigeria’s Poverty Crisis: A World Bank Perspective on the Deepening Divide.
George Omagbemi Sylvester | SaharaWeeklyNG.com
Half of Nigerians Are Now Poor And the Numbers Are Set to Worsen.
Introduction.
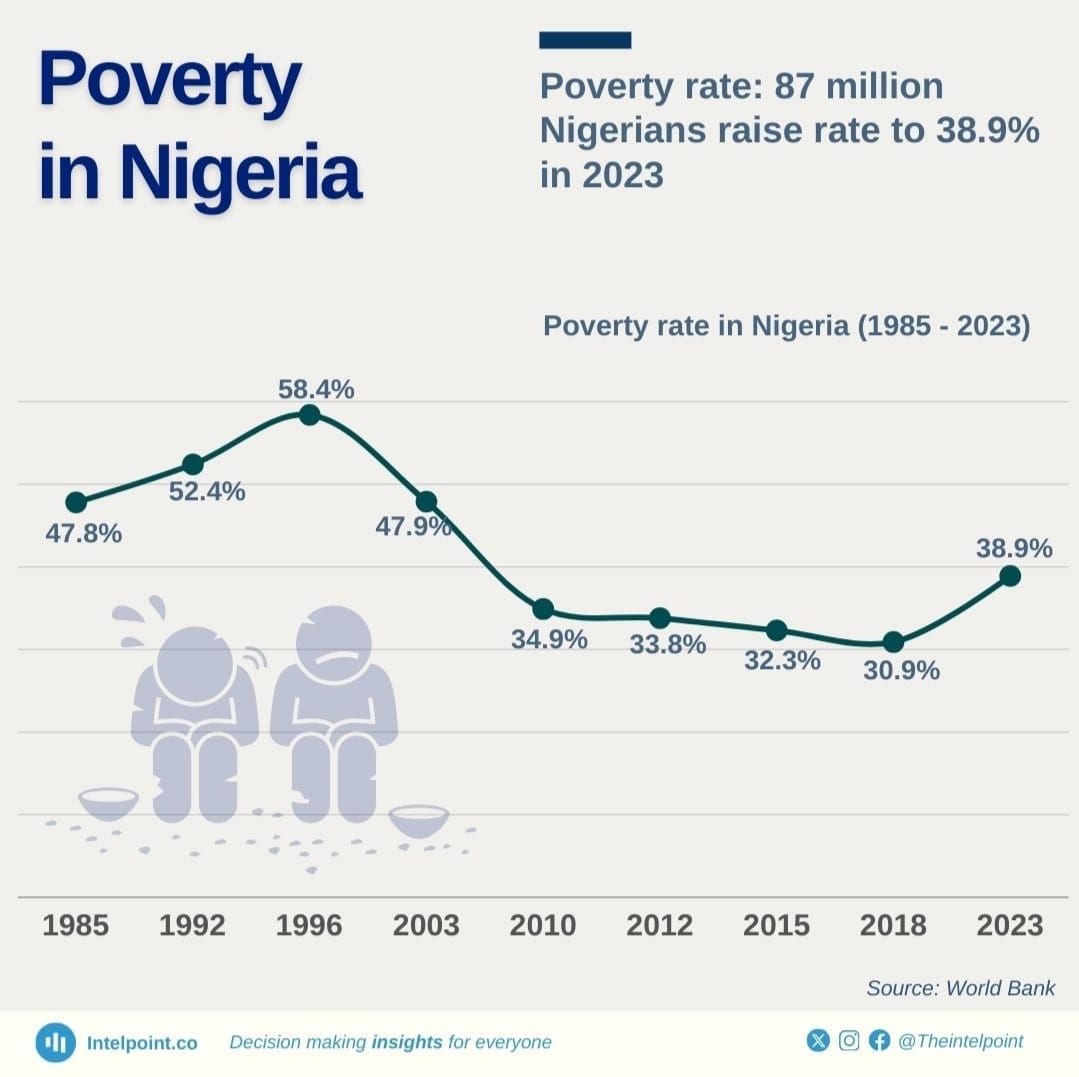
Nigeria, Africa’s most populous nation and one of its largest economies, stands at a crossroads. Despite abundant natural resources, trillions of naira in revenue and successive economic reform programs, nearly half of its population is trapped in poverty. The latest World Bank data paints a stark picture, 46% of Nigerians lived below the poverty line in 2024, with projections indicating that 52.5% could fall into extreme poverty by 2025. This is not merely a statistic; but a humanitarian crisis, a warning signal for policymakers and a stark indictment of decades of economic mismanagement.
The Stark Reality: Rising Poverty in Nigeria.
The World Bank’s October 2025 Poverty & Equity Brief underscores that Nigeria is sliding deeper into poverty. Food inflation, which disproportionately affects low-income households spending up to 70% of their income on essentials, has been a major driver. The depreciation of the naira has compounded the problem, making imports prohibitively expensive, squeezing household purchasing power and forcing millions into deprivation.
George O. Sylvester encapsulates this harsh reality with piercing clarity: “You cannot borrow your way out of poverty. You must produce your way to prosperity.” This statement resonates today more than ever. Successive governments reliance on external borrowing, often without creating productive industries or jobs, has left Nigeria with towering debt and a declining standard of living for its citizens. Production, entrepreneurship and wealth creation must replace borrowing as the engine for sustainable poverty alleviation.
Structural Barriers Hindering Poverty Reduction.
The World Bank’s 2022 Poverty Assessment highlights structural deficiencies that stymie progress. Nigeria suffers from sluggish economic growth, insufficient human capital development, weak labor markets and vulnerability to external shocks such as climate disasters and regional conflicts.
Economic growth, while occurring intermittently, has not been inclusive. Wealth remains concentrated among elites and in specific regions, while northern states face disproportionately high poverty levels. Infrastructure deficits, inadequate healthcare and underfunded education systems exacerbate inequality, creating a cycle where the poor remain trapped while the rich consolidate wealth.
Inflation and Currency Depreciation: Pushing Nigerians into Poverty.
The inflationary spiral in Nigeria has been brutal. Food prices have soared, energy costs have risen and the naira has lost substantial value against major currencies. This triple pressure has disproportionately impacted the poor. According to the World Bank, households already living near the poverty line are now being pushed below it, a phenomenon economists term “NEW POVERTY ENTRANTS.”
Professor Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala, former Nigerian Finance Minister, has consistently emphasized that currency stability, inflation control and domestic production are critical. Without addressing these factors, any attempt to reduce poverty through subsidies or borrowing is temporary and unsustainable.
The Role of Employment and Social Protection.
Social protection programs, while conceptually promising, have been undermined by poor targeting, corruption and inadequate funding. Programs like the National Social Investment Programmes (NSIP) have helped some communities, but millions of Nigerians remain excluded.
Simultaneously, the labor market fails to absorb new entrants, resulting in high unemployment and underemployment rates, especially among youths. A growing population of idle, educated youth becomes both an economic and social risk, fueling urban poverty, crime and social unrest.
Renowned economist Justin Yifu Lin observes, “Inclusive growth is the key to poverty reduction.” Economic expansion must be paired with deliberate policies to empower the poorest. Nobel laureate Amartya Sen adds that expanding individual capabilities through investment in education, healthcare and social infrastructure is central to sustainable poverty alleviation.
Regional Disparities: North vs. South.
The poverty divide between northern and southern Nigeria remains stark. Northern states face higher rates of extreme poverty, compounded by insecurity, poor infrastructure, low literacy levels and weak governance. Southern states, particularly in oil-rich regions, have higher income levels but also stark pockets of inequality.
Without deliberate interventions, these regional disparities will persist, creating long-term political, social and economic instability. The World Bank stresses the need for localized development policies, targeted social programs and investment in human capital to bridge this divide.
Debt Dependency vs. Productive Growth.
Nigeria’s debt-to-GDP ratio has risen sharply in recent years, largely to service budget deficits rather than fund productive sectors. This approach perpetuates a vicious cycle of borrowing temporarily plugs fiscal gaps but does not create jobs or industries, leaving poverty unabated.
Here, Sylvester’s quote resonates powerfully: “You cannot borrow your way out of poverty. You must produce your way to prosperity.” Any sustainable anti-poverty strategy must prioritize domestic production, value-added industries and entrepreneurship. Only through production-driven growth can Nigeria create employment, generate revenue and reduce dependence on loans.
Climate Change and External Shocks: Hidden Threats.
Nigeria’s vulnerability to climate change (manifested through flooding, desertification and agricultural disruption) directly impacts poverty. Poor households, largely dependent on subsistence farming, are hit hardest. Similarly, security crises, such as the Boko Haram insurgency and banditry in northern states, displace millions, disrupting livelihoods and deepening poverty.
The World Bank emphasizes that social protection alone cannot counter these shocks. Strengthening resilience through infrastructure investment, disaster preparedness and diversification of local economies is critical.
The Urgency of Reform: A Call to Action.
The World Bank’s reports are clear, Nigeria is at a tipping point. Without comprehensive reforms, poverty will become entrenched, with nearly 53% of Nigerians projected to live in extreme poverty by 2025.
Key measures include:
Boosting production and industrialization – to generate jobs and reduce reliance on imports.
Strengthening social protection programs – with precise targeting and sufficient funding.
Improving education and healthcare – to expand human capital and capabilities.
Controlling inflation and stabilizing the naira – to protect purchasing power.
Addressing regional disparities – through localized policies that prioritize underdeveloped areas.
As Sylvester warns, the path to prosperity is PRODUCTION-DRIVEN, not DEBT-DRIVEN. Borrowing may provide temporary relief, but only meaningful investment in productive sectors can create jobs, raise incomes and lift millions out of poverty.
The Bottom Line.
Nigeria’s poverty crisis is not inevitable; it is the product of policy failure, structural inefficiency and governance challenges. The World Bank’s data presents both a warning and an opportunity. Urgent, evidence-based reforms, focused on inclusive growth and production, are imperative. As George Omagbemi Sylvester states emphatically: “You cannot borrow your way out of poverty. You must produce your way to prosperity.”
The nation’s future depends on decisive action today; otherwise, millions of Nigerians will be condemned to poverty for generations.
Business
Harmony Gardens’ Ibeju-Lekki Portfolio Crosses $1bn

Harmony Gardens’ Ibeju-Lekki Portfolio Crosses $1bn
Harmony Garden & Estate Development Limited has expanded its development activities across Ibeju-Lekki, pushing the projected long-term value of its estate portfolio beyond $1 billion.
Led by Chief Executive Officer Hon. Dr. Audullahi Saheed Mosadoluwa, popularly know Saheed Ibile, the company is developing seven estates within the Lekki–Ibeju corridor. Details available on Harmony Garden & Estate Development show a portfolio spanning land assets and ongoing residential construction across key growth locations.
A major component is Lekki Aviation Town, where urban living meets neighborhood charm, located near the proposed Lekki International Airport and valued internally at over $250 million. The development forms part of the company’s broader phased expansion strategy within the axis.
Other estates in the corridor tagged as the “Citadel of Joy” (Ogba-idunnu) include Granville Estate, Majestic Bay Estate, The Parliament Phase I & II, and Harmony Casa Phase I & II.
With multiple projects active, the rollout of the Ibile Traditional Mortgage System, and structured expansion underway, Harmony Garden & Estate Development Ltd continues to deepen its presence within the fast-growing Ibeju-Lekki real estate market.
Business
BUA Group Showcases Food Manufacturing Strength at 62nd Paris International Agricultural Show

BUA Group Showcases Food Manufacturing Strength at 62nd Paris International Agricultural Show
BUA Group, one of Africa’s leading diversified conglomerates, is maintaining a strong presence at the ongoing 62nd edition of the Paris International Agricultural Show in France, participating as a premium sponsor and supporting the Nigeria Pavilion at one of the world’s most respected agricultural gatherings.
The 62nd Paris International Agricultural Show, taking place from February 21 to March 1, 2026, at Porte de Versailles in Paris, convenes global leaders across farming, agro processing, technology, finance, and policy. The event serves as a strategic platform for industry engagement, knowledge exchange, and commercial partnerships shaping the future of global food systems.
BUA Group’s participation reflects its long term commitment to strengthening the entire food production value chain. Through sustained investments in large scale processing, value addition, and branded consumer products, the Group continues to reinforce its role in advancing food security, industrial growth, and regional trade integration.
Speaking on the Group’s participation, the Executive Chairman of BUA Group, Abdul Samad Rabiu CFR, said, “BUA’s presence at the Paris International Agricultural Show reflects our belief that Africa must be an active participant in shaping the future of global food systems. We have invested significantly in local production capacity because we understand that food security, industrial growth, and economic resilience are interconnected. Platforms like this allow us to build partnerships that strengthen Nigeria’s competitiveness and expand our reach beyond our borders.”
BUA Foods, a subsidiary of BUA Group, maintains a strong footprint in flour, pasta, spaghetti, sugar, and rice production, serving millions of consumers within Nigeria and across neighbouring African markets. The Managing Director of BUA Foods, Engr. Abioye Ayodele, representing the Executive Chairman, is attending the event at the Nigeria Pavilion, engaging industry stakeholders and showcasing the company’s manufacturing capabilities.
Also speaking at the show, Engr. Ayodele stated, “BUA Foods has built scale across key staple categories that are central to household consumption. Our participation at this Show allows us to demonstrate the quality, consistency, and operational strength behind our products. We are also engaging global stakeholders with a clear message that Nigerian manufacturing can meet international standards while serving both domestic and regional markets efficiently.”
The Show provides BUA Group with an opportunity to deepen trade relationships, explore new export pathways, and reinforce Nigeria’s growing relevance within the global agricultural and food ecosystem.
BUA Group remains focused on building enduring institutions, expanding productive capacity, and positioning African enterprise competitively within global markets.
Business
Nigeria’s Inflation Drops to 15.10% as NBS Reports Deflationary Trend

Nigeria’s headline inflation rate declined to 15.10 per cent in January 2026, marking a significant drop from 27.61 per cent recorded in January 2025, according to the latest Consumer Price Index (CPI) report released by the National Bureau of Statistics.
The report also showed that month-on-month inflation recorded a deflationary trend of –2.88 per cent, representing a 3.42 percentage-point decrease compared to December 2025. Analysts say the development signals easing price pressures across key sectors of the economy.
Food inflation stood at 8.89 per cent year-on-year, down from 29.63 per cent in January 2025. On a month-on-month basis, food prices declined by 6.02 per cent, reflecting lower costs in several staple commodities.
The data suggests a sustained downward trajectory in inflation over the past 12 months, pointing to improving macroeconomic stability.
The administration of President Bola Ahmed Tinubu has consistently attributed recent economic adjustments to ongoing fiscal and monetary reforms aimed at stabilising prices, boosting agricultural output, and strengthening domestic supply chains.
Economic analysts note that while the latest figures indicate progress, sustaining the downward trend will depend on continued policy discipline, exchange rate stability, and improvements in food production and distribution.
The January report provides one of the clearest indications yet that inflationary pressures, which surged in early 2025, may be moderating.
-

 celebrity radar - gossips6 months ago
celebrity radar - gossips6 months agoWhy Babangida’s Hilltop Home Became Nigeria’s Political “Mecca”
-

 society5 months ago
society5 months agoReligion: Africa’s Oldest Weapon of Enslavement and the Forgotten Truth
-

 society6 months ago
society6 months agoPower is a Loan, Not a Possession: The Sacred Duty of Planting People
-

 news7 months ago
news7 months agoTHE APPOINTMENT OF WASIU AYINDE BY THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AS AN AMBASSADOR SOUNDS EMBARRASSING